Dapper SimpleCRUD Read Data
Most of the applications would perform the basic operation to retrieve data from the database and display the results. We have two tables in the database that contains the following data.
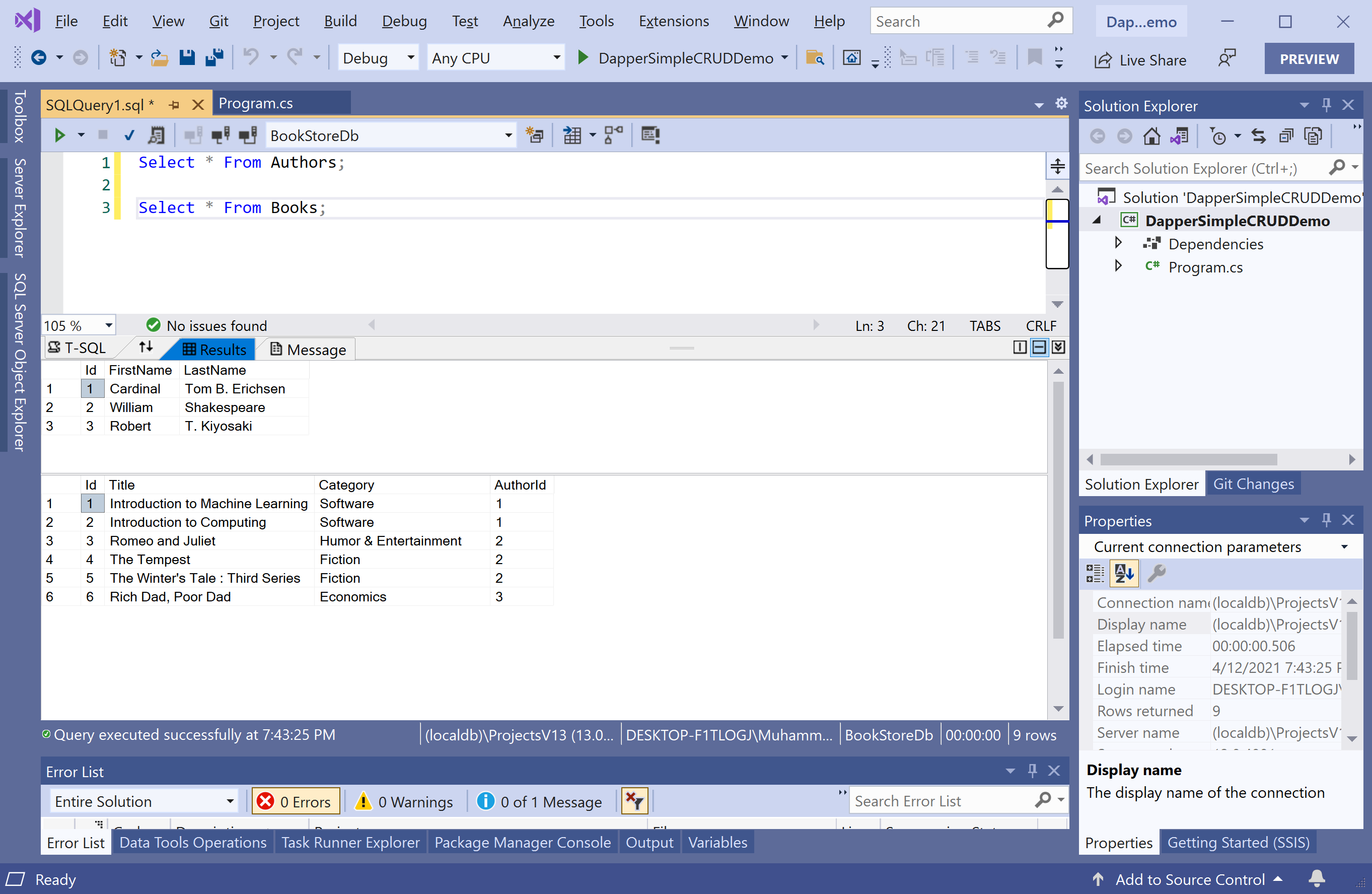
To retrieve the data from the database using Dapper.SimpleCRUD, let's create two classes called Author and Book.
Here is the implementation of the Author class.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DapperSimpleCRUDDemo
{
public class Author
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public List<Book> Books { get; set; }
}
}
The following is the implementation of the Book class.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DapperSimpleCRUDDemo
{
public class Author
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public List<Book> Books { get; set; }
}
}
In the Program class, define the static variable, which contains the connection string of the database.
static string ConnectionString = @"Data Source=(localdb)\ProjectsV13;Initial Catalog=BookStoreDb;Integrated Security=True;";
The first step is to create a member of type IDbConnection with the SqlConnection by passing the connection string.
private static List<Author> GetAllAuthors()
{
using (IDbConnection db = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
List<Author> authors = db.GetList<Author>().ToList();
return authors;
}
}
The GetList extension method enables you to retrieve data from the database and populate data in your object model.
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<Author> authors = GetAllAuthors();
foreach (var author in authors)
{
Console.WriteLine(author.FirstName + " " + author.LastName);
}
}
Let's execute the above code, and you will see the following error.
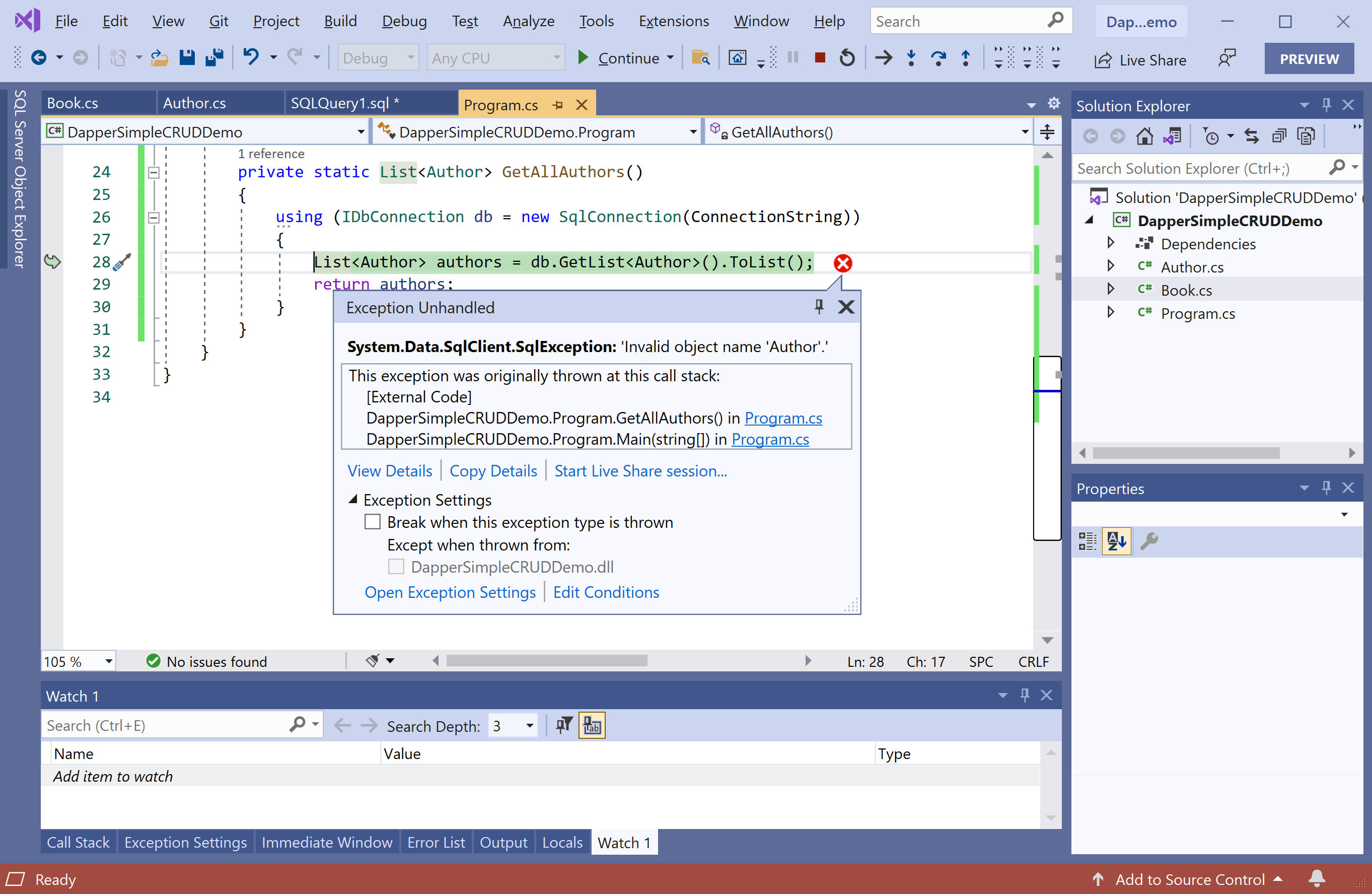
That is because we have a class called Author, and the table name is Àuthors in the database. The class name and table must match, which isn't the case here, so let's use the Table attribute to map the Author class to the Authors table.
[Table("Authors")]
public class Author
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public List<Book> Books { get; set; }
}
Similarly, specify the Table attribute in the Book class as well. Let's execute the above code again, and you will see the following output.
Cardinal Tom B. Erichsen
William Shakespeare
Robert T. Kiyosakiy
You can also specify the where conditions using the anonymous object and map the results to a strongly typed list.
private static List<Book> GetAllBooks(string category)
{
using (IDbConnection db = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
List<Book> books = db.GetList<Book>(new { Category = category }).ToList();
return books;
}
}
You can also specify the where clause and map the results to a strongly typed list.
private static List<Book> GetAllBooks(string category)
{
using (IDbConnection db = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
//List<Book> books = db.GetList<Book>(new { Category = category }).ToList();
List<Book> books = db.GetList<Book>("where Category = @Category", new { Category = category }).ToList();
return books;
}
}
Let's pass the "Fiction" as a parameter as shown below.
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<Book> fictionBooks = GetAllBooks("Fiction");
foreach (var book in fictionBooks)
{
Console.WriteLine(book.Title);
}
}
Let's execute the above code, and you will see the following books from fiction category.
The Tempest
The Winter's Tale : Third Series
