Dapper SimpleSave Database Setup
To use Dapper.SimpleSave, we need to create a database first, and then we will perform various database operations using the Dapper.SimpleSave library.
The SQL CREATE DATABASE statement is used to create a new SQL database.
USE [master]
GO
CREATE DATABASE [BookStoreDb]
GO
USE [BookStoreDb]
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Authors](
[Id] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[FirstName] [nvarchar](450) NULL,
[LastName] [nvarchar](450) NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Authors] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[Id] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Books](
[Id] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[Title] [nvarchar](450) NULL,
[Category] [nvarchar](max) NULL,
[AuthorId] [int] NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Books] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[Id] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY] TEXTIMAGE_ON [PRIMARY]
GO
It will create a BookStoreDb database that contains two tables. Now we need to insert some data into these tables, which can be used later.
The following SQL statements insert new records in the Authors and Books tables.
USE [BookStoreDb]
GO
INSERT INTO Authors(FirstName, LastName) VALUES ('Cardinal','Tom B. Erichsen');
INSERT INTO Authors(FirstName, LastName) VALUES ('William','Shakespeare');
INSERT INTO Authors(FirstName, LastName) VALUES ('Robert','T. Kiyosaki');
INSERT INTO Books(Title, Category, AuthorId) VALUES ('Introduction to Machine Learning', 'Software', 1);
INSERT INTO Books(Title, Category, AuthorId) VALUES ('Introduction to Computing', 'Software', 1);
INSERT INTO Books(Title, Category, AuthorId) VALUES ('Romeo and Juliet', 'Humor & Entertainment', 2);
INSERT INTO Books(Title, Category, AuthorId) VALUES ('The Tempest', 'Fiction', 2);
INSERT INTO Books(Title, Category, AuthorId) VALUES ('The Winter''s Tale : Third Series', 'Fiction', 2);
INSERT INTO Books(Title, Category, AuthorId) VALUES ('Rich Dad, Poor Dad', 'Economics', 3);
Let's try the following queries to test the data in the database.
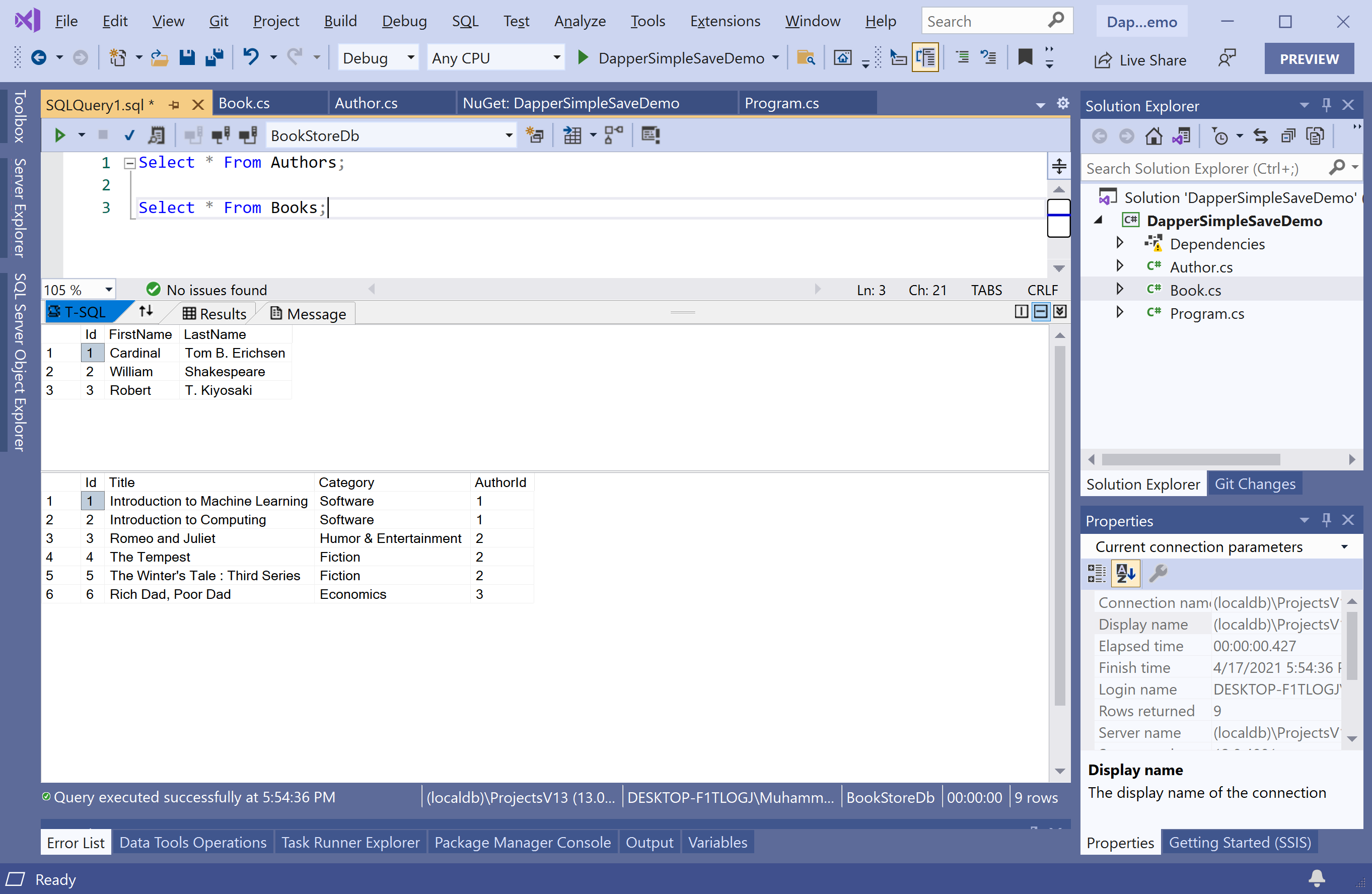
Select * From Authors;
Select * From Books;
Let's click on the Execute button, and you will see the results of the above queries.
Let's create two classes called Author and Book.
Here is the implementation of the Author class.
using Dapper.SimpleSave;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DapperSimpleSaveDemo
{
[Table("Authors")]
public class Author
{
[PrimaryKey]
public int? Id { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
[OneToMany]
public List<Book> Books { get; set; }
}
}
The following is the implementation of the Book class.
using Dapper.SimpleSave;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DapperSimpleSaveDemo
{
[Table("Books")]
public class Book
{
[PrimaryKey]
public int? Id { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Category { get; set; }
public int AuthorId { get; set; }
}
}
In the Program class, define the static variable, which contains the connection string of the database.
static string ConnectionString = @"Data Source=(localdb)\ProjectsV13;Initial Catalog=BookStoreDb;Integrated Security=True;";
