EF Core Naming Conventions Database Setup
Create Data Model
Model is a collection of classes to interact with the database.
- A model stores data retrieved according to the commands from the Controller and displayed in the View.
- It can also be used to manipulate the data to implement the business logic.
To create a data model for our application, we will start with the following two entities.
- Book
- Author
There's a one-to-many relationship between Author and Book entities. In other words, an author can write any number of books, and a book can be written by only one author.
Create Author Entity
We will create a class called Author and add the following code.
public class Author
{
public int AuthorId { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Book> Books { get; set; }
}
The AuthorId property will become the primary key column of the database table that corresponds to this class. By default, Entity Framework interprets a property that's named Id or <classname>Id as the primary key.
- The
Booksproperty is a navigation property. Navigation properties hold other entities related to this entity. - In this case, the
Booksproperty of anAuthorentity will hold all of theBookentities related to thatAuthorentity. - In other words, if a given
Authorrow in the database has two relatedBookrows, thatAuthorentity'sBooksnavigation property will contain those twoBookentities.
Create Book Entity
Now let's add another entity class Book, and replace the following code.
public class Book
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public int NoOfPages { get; set; }
public int AuthorId { get; set; }
public Author Author { get; set; }
}
- The
Idproperty will be the primary key; this entity uses theIdpattern instead of<classname>Idby itself, as you saw in theAuthorentity. - Usually, you would choose one pattern and use it throughout your data model.
- Here, the variation illustrates that you can use either pattern.
Create Database Context
The database context class provides the main functionality to coordinate Entity Framework with a given data model.
- You can create this class by deriving from the
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.DbContextclass. - In your code, you can specify which entities are included in the data model.
- You can also customize certain Entity Framework behavior.
So let's create a folder in your project by right-clicking your project in Solution Explorer and clicking Add > New Folder. Name the folder DAL (Data Access Layer). In that folder, create a new class file named BookStore.cs, and replace the following code.
public class BookStore : DbContext
{
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(@"Data Source=(localdb)\ProjectsV13;Initial Catalog=BookStoreDb;");
}
public DbSet<Author> Authors { get; set; }
public DbSet<Book> Books { get; set; }
}
This code creates a DbSet property for each entity set. In Entity Framework terminology, an entity set typically corresponds to a database table, and an entity corresponds to a row in the table.
Initialize Database
The Entity Framework will create an empty database for you. So we need to write a method called after the database is created to populate it with test data.
public static void Initialize()
{
using (BookStore context = new BookStore())
{
context.Database.EnsureDeleted();
context.Database.EnsureCreated();
}
}
- The above code creates a database when needed and loads test data into the new database.
- It also checks if there are any authors in the database, and if not, it assumes the database is new and needs to be seeded with test data.
In the Main method, replace the following code.
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Initialize();
}
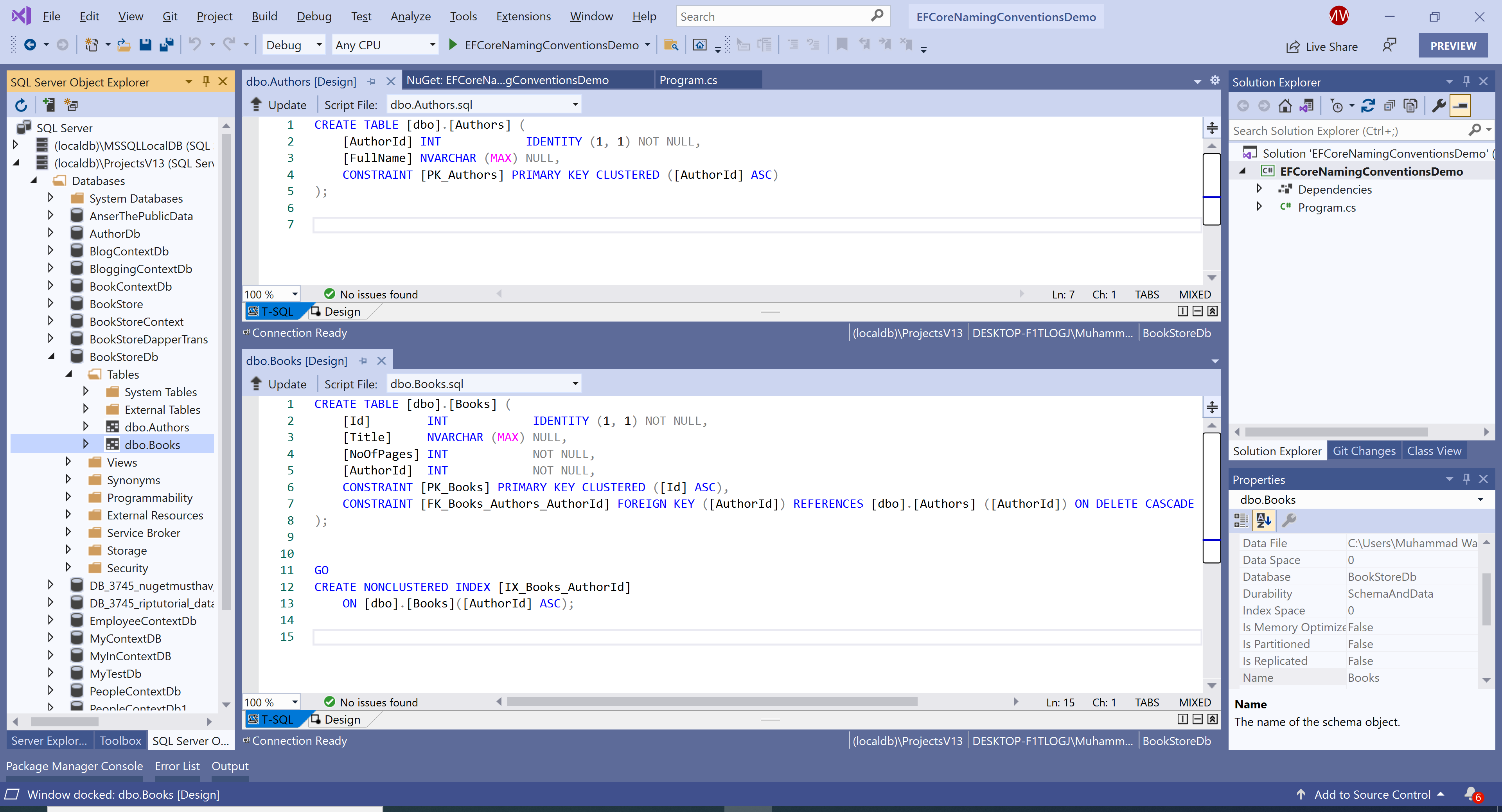
When you run your application for the first time, the database will be created containing the following tables and columns with the default naming conventions.