EF Core Advanced Topics Shadow Properties
In Entity Framework Core, shadow properties are properties that are not defined in the entity class but can be included in the model and are mapped to database columns.
- It means that we can have columns for these properties in our tables, but we will not have a corresponding property field in our entity class.
- The value and state of these properties are maintained purely in the Change Tracker.
- These are useful when there is data in the database that should not be exposed to the mapped entity types.
Foreign Key Shadow Properties
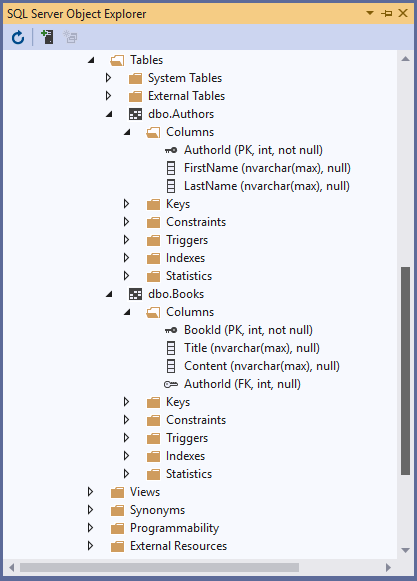
In most cases, shadow properties are used for foreign key properties, where the relationship between two entities is represented by a foreign key value in the database, but the relationship is managed on the entity types using navigation properties between the entity types.
- By convention, EF will introduce a shadow property when a relationship is discovered but no foreign key property is found in the dependent entity class.
- The property will be named
<navigation_property_name><principal_key_property_name>, but if the principal key property name includes the name of the navigation property, then the name will just be<principal_key_property_name>. - If there is no navigation property on the dependent entity, then the principal type name is used in its place.
public class Author
{
public int AuthorId { get; set; }
public string Url { get; set; }
public List<Book> Books { get; set; }
}
public class Book
{
public int BookId { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Content { get; set; }
// Since there is no CLR property that holds the foreign
// key for this relationship, a shadow property is created.
public Author Author { get; set; }
}
class MyContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Author> Authors { get; set; }
public DbSet<Book> Books { get; set; }
}
The above code creates a shadow property called AuthorId to the Book entity.
Define Shadow Properties
To define the shadow properties, you can use the Fluent API in the OnModelCreating using the Property method for an entity type. After calling the string overload of the Property method, you can chain any of the configurations calls for other properties as well.
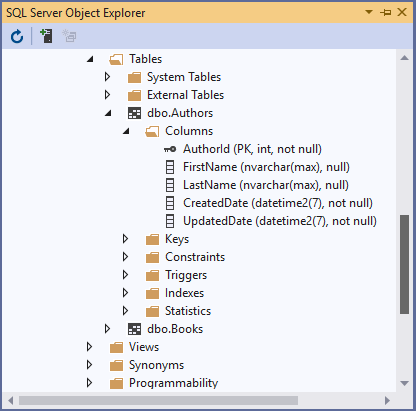
The following code configures two shadow properties CreatedDate and UpdatedDate on the Author entity.
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Author>().Property<DateTime>("CreatedDate");
modelBuilder.Entity<Author>().Property<DateTime>("UpdatedDate");
}
The Property method is used to configure a shadow property by specifying the name of the shadow property as a string and the type as a generic parameter. If the name specified in the Property method matches the name of an existing property, then the EF Core will configure that existing property as a shadow property rather than introducing a new shadow property.
Access Shadow Properties
You can access a shadow property through the ChangeTracker API using the Property method of EntityEntry.
using (var context = new MyContext())
{
var author = new Author { FirstName = "John", LastName = "Doe" };
context.Add(author);
context.Entry(author).Property("CreatedDate").CurrentValue = DateTime.UtcNow;
context.SaveChanges();
}
You can reference shadow properties in LINQ queries using the EF.Property static method as shown below.
using (var context = new MyContext())
{
var authors = context.Authors
.OrderBy(a => EF.Property<DateTime>(a, "UpdatedDate"))
.ToList();
}
You can't access shadow properties after a no-tracking query since the entities returned are not tracked by the change tracker.
