EF Core with Android Overview
Nowadays, in any application development data plays an important part and mobile apps are no exception. In mobile applications, developers make an important decision on how to handle data. There are many options available, but one that .NET developers are often especially familiar with is the Entity Framework.
What is Entity Framework?
Entity Framework is an ORM that enables .NET developers to work with a database using .NET objects and eliminates the need for more of the data-access code that developers usually need to write. Entity Framework is great but was difficult to use in mobile development projects until Entity Framework Core was released.
What is Entity Framework Core?
Entity Framework Core is a lightweight, extensible, cross-platform version of Entity Framework data access technology.
- EF Core introduces many new features and improvements when compared to full-scale Entity Framework but is a completely brand-new codebase that’s optimized for cross-platform applications.
- If you have experience with Entity Framework, you’ll find EF Core very familiar.
- It doesn’t have all the features, and many will show up in future releases, such as lazy loading and connection resiliency.
- Because EF Core is .NET Standard-compatible, we can now use it with Xamarin.Android.
What is Android?
Android is an open-source operating system based on the Linux kernel. Android was originally developed by Android Inc. and subsequently purchased by Google. Android provides a rich application framework that allows you to build innovative apps and games for mobile devices.
Xamarin.Android
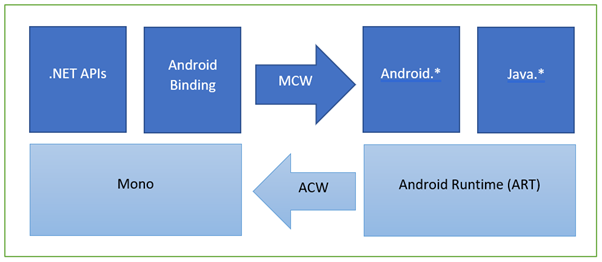
- Xamarin.Android applications compile from C# into Intermediate Language (IL) which is then Just-in-Time (JIT) compiled to a native assembly when the application launches.
- Xamarin.Android applications run within the Mono execution environment, side by side with the Android Runtime (ART) virtual machine.
- Xamarin provides .NET bindings to the Android.* and Java.* namespaces.
- The Mono execution environment calls into these namespaces via Managed Callable Wrappers (MCW) and provides Android Callable Wrappers (ACW) to the ART, allowing both environments to invoke code in each other.