EF Core with Android Add Views
In the Xamarin.Forms, views are the building blocks of cross-platform mobile user interfaces. Views are user-interface objects such as labels, buttons, and sliders that are commonly known as controls or widgets in other graphical programming environments.
Let’s create a Views folder and then add a content page.
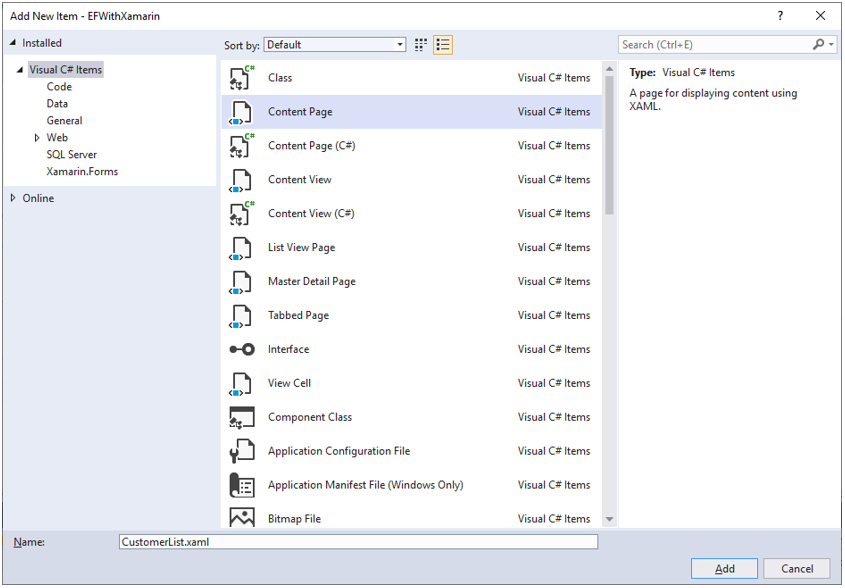
Enter CustomerList.xaml in the name field and click Add button. Remove all the template code and add the following code in CustomerList.xaml.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<ContentPage xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms/design"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="Customers"
x:Class="EFWithXamarin.Views.CustomerList">
<ContentPage.ToolbarItems>
<ToolbarItem Text="+"
Clicked="OnCustomerAddedClicked" />
</ContentPage.ToolbarItems>
<ListView x:Name="listView"
Margin="20"
ItemSelected="OnListViewItemSelected">
<ListView.ItemTemplate>
<DataTemplate>
<TextCell Text="{Binding Name}"
Detail="{Binding Description}" />
</DataTemplate>
</ListView.ItemTemplate>
</ListView>
</ContentPage>
Let’s open the CustomerList.xaml.cs and replace the following code in OnAppearing() method.
protected override void OnAppearing()
{
base.OnAppearing();
EntityFrameworkService entityFrameworkService = new EntityFrameworkService();
listView.ItemsSource = entityFrameworkService.GetAll();
}
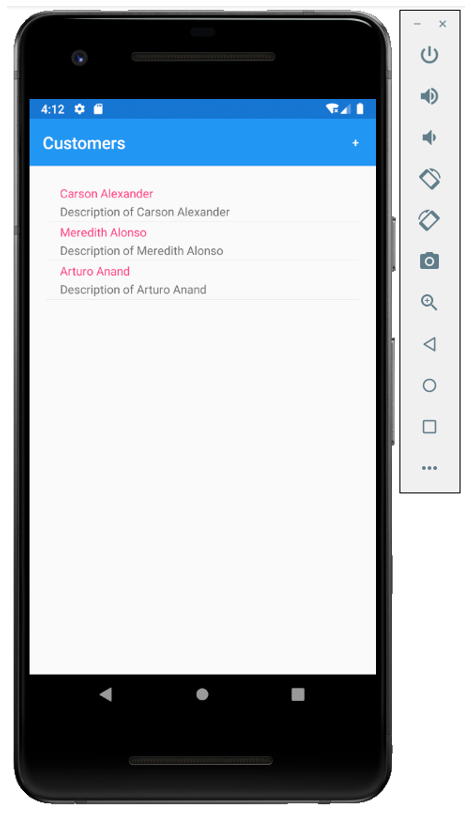
It will assign the list of customers from the database to the list view defined in the xaml file.
Now open the App.xaml.cs file and in the constructor, you can see the following code.
public App()
{
InitializeComponent();
MainPage = new NavigationPage(new MainPage());
}
Now if you run your application you will see the MainPage, but here we want to load CustomerList.xaml as the first so let’s replace the following code.
public App()
{
InitializeComponent();
MainPage = new NavigationPage(new CustomerList());
}
Now let’s seed the database with dummy data in the OnStart() method using the following code.
using EFWithXamarin.Data;
using EFWithXamarin.Models;
using EFWithXamarin.Views;
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
using System.IO;
using Xamarin.Forms;
namespace EFWithXamarin
{
public partial class App : Application
{
public App()
{
InitializeComponent();
MainPage = new NavigationPage(new CustomerList());
}
protected override void OnStart()
{
using (var context = new EntityContext())
{
if (!File.Exists(context.DbPath))
{
context.Database.EnsureCreated();
context.Customers.Add(new Customer()
{
Name = "Carson Alexander",
Description = "Description of Carson Alexander",
IsActive = false,
PhoneContacts = new ObservableCollection<PhoneContact>()
{
new PhoneContact() { PhoneNumber = "333-5555555" },
new PhoneContact() { PhoneNumber = "333-6666666" }
}
});
context.Customers.Add(new Customer()
{
Name = "Meredith Alonso",
Description = "Description of Meredith Alonso",
IsActive = false,
PhoneContacts = new ObservableCollection<PhoneContact>()
{
new PhoneContact() { PhoneNumber = "444-7777777" },
}
});
context.Customers.Add(new Customer()
{
Name = "Arturo Anand",
Description = "Description of Arturo Anand",
IsActive = false,
PhoneContacts = new ObservableCollection<PhoneContact>()
{
new PhoneContact() { PhoneNumber = "555-2222222" },
}
});
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
}
protected override void OnSleep()
{
}
protected override void OnResume()
{
}
}
}
Let’s run your application and you will see all the customers on the first page.