EF Core with Ubuntu Add Entity Framework Core Functionality
Entity Framework is a lightweight ORM and simplifies mappings between your .NET objects and the tables and columns in your relational database.
It is widely used and well known for the following features.
- Rich mapping capabilities and has support for one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships.
- Support for inheritance, complex types as well as stored procedures.
- A possibility of using only code, the so-called “Code-First” approach (including setting up the database and interacting with tables and columns only through code).
- It offers a visual designer for creating entity models.
- It offers excellent integration with ASP.NET Framework.
- Support for eager, lazy, and explicit loading.
Install EF Core
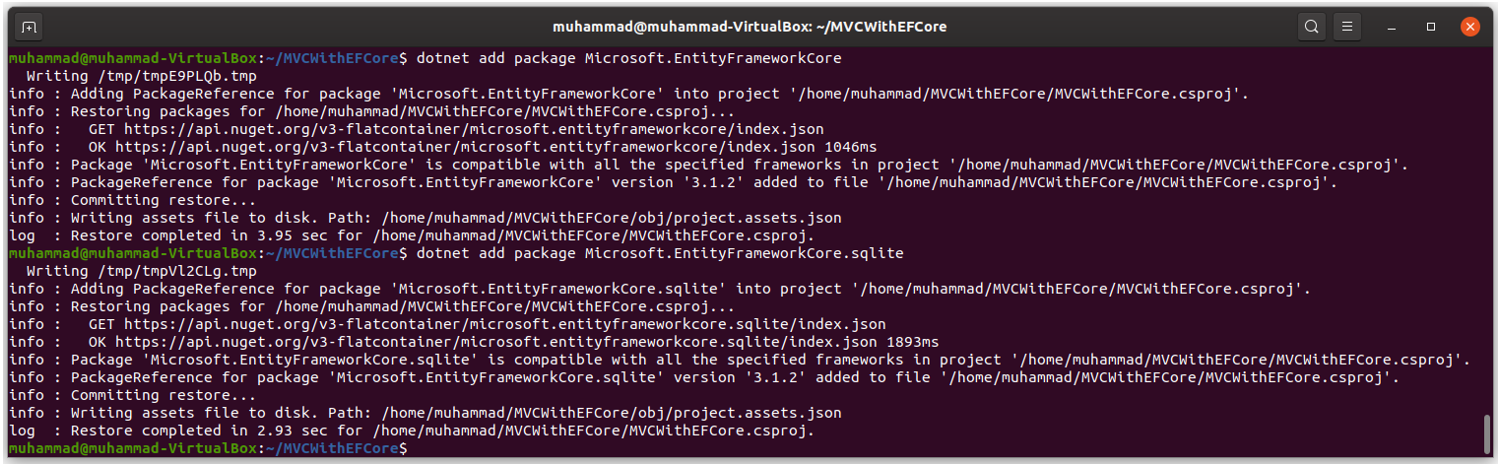
To install EF Core, open the terminal and go to the project folder and run the following commands.
dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore
dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Sqlite
We are ready to start writing some Entity Framework code.
Create a Model
The model plays a significant part in the Entity Framework. It contains configurations, mapping properties, relationships, and defines which objects map to which tables. Let’s open the Visual Code and open the project folder in it.
Let’s add a new class Customer to the Models folder.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace MVCWithEFCore.Models
{
public class Customer
{
public int CustomerID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public Boolean IsActive { get; set; }
public List<PhoneContact> PhoneContacts { get; set; }
public Customer()
{
PhoneContacts = new List<PhoneContact>();
}
}
}
Now add another class in the Models and call it PhoneContact.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MVCWithEFCore.Models
{
public class PhoneContact
{
public int PhoneContactID { get; set; }
public string PhoneNumber { get; set; }
public int CustomerID { get; set; }
public Customer Customer { get; set; }
}
}
Define the DbContext
If you have used Entity Framework before, you will know how to define a DbContext and the underlying Models that define a database schema. We have already created a simple model that has Customer and PhoneContact classes, now let’s ensure that these classes are part of the DbContext by defining a new context called EntityContext.
So first we will create a new folder called Data and add an EntityContext class in that folder.
using Microsoft.Data.Sqlite;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using MVCWithEFCore.Models;
using System;
namespace MVCWithEFCore.Data
{
public class EntityContext : DbContext
{
public static string DbPath = "DbMy.db";
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
optionsBuilder.UseSqlite("Data Source=" + DbPath);
}
public DbSet<Customer> Customers { get; set; }
public DbSet<PhoneContact> PhoneContacts { get; set; }
}
}
In ASP.NET Core, services such as the DB context must be registered with the dependency injection (DI) container. The container provides the service to controllers, so we need to update ConfigureServices in Startup.cs file with the following code.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllers();
services.AddDbContext<EntityContext>(options => options.UseSqlite("Data Source="+ EntityContext.DbPath));
}
