Dapper Transaction Related Data
So far, we have performed operations on a single row. But what if you need to deal with more complex objects that have parent-child relationships. Let's consider our example; we have a one-to-many relationship between an Author and Book. It means a single author can have many books.
If you look at the Author class, you can see a list of books.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DapperTransactionDemo
{
class Author
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public List<Book> Books { get; set; }
}
}
In an Authors table, you can see on the first row William Shakespeare has an Id = 2.
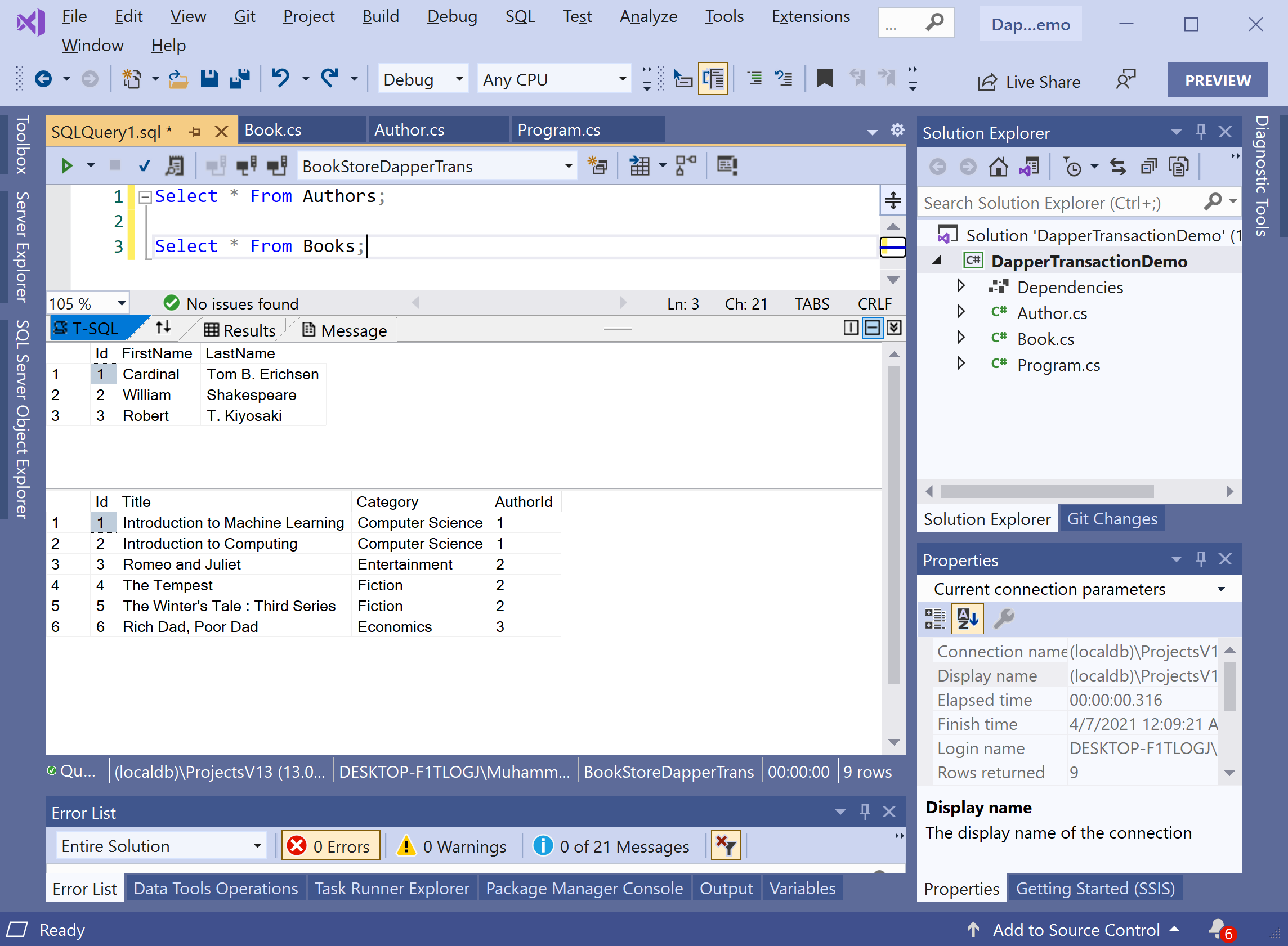
If you look in the Books table, you can see three different rows that have an AuthorId of 2. So it means, William Shakespeare has written multiple books.
So let's retrieve the authors from a database and their respective books using the QueryMultiple extension method. It can execute multiple queries within the same command and map results.
private static Author GetAuthorAndTheirBooks(int id)
{
string sql =
"SELECT * FROM Authors WHERE Id = @Id;" +
"SELECT * FROM Books WHERE AuthorId = @Id;";
using (IDbConnection connection = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
connection.Open();
using (var transaction = connection.BeginTransaction())
{
using (var results = transaction.QueryMultiple(sql, new { Id = id }))
{
var author = results.Read<Author>().SingleOrDefault();
var books = results.Read<Book>().ToList();
if (author != null && books != null)
{
author.Books = books;
}
return author;
}
}
}
}
You can see that first, we have specified two different SELECT statements, the first one for the individual author and the second one for the author's books.
- The
QueryMultipleis an extension method that returns multiple result sets in the query results of typeGridReader. - We simply need to call the
Readmethod on that object multiple times to get the author record and then for books.
Let's call the GetAuthorAndTheirBooks method in the Main method.
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Author author = GetAuthorAndTheirBooks(2);
Console.WriteLine(author.FirstName + " " + author.LastName);
foreach (var book in author.Books)
{
Console.WriteLine("\t Title: {0} \t Category: {1}", book.Title, book.Category);
}
}
Let's execute the above code, and you will see the following output.
William Shakespeare
Title: Romeo and Juliet Category: Entertainment
Title: The Tempest Category: Fiction
Title: The Winter's Tale : Third Series Category: Fiction
