EF Core with MVC Basic CRUD Functionality
In this article, we will customize the create, read, update, delete (CRUD) code that the MVC scaffolding automatically creates for you in controllers and views. Let's run your application.
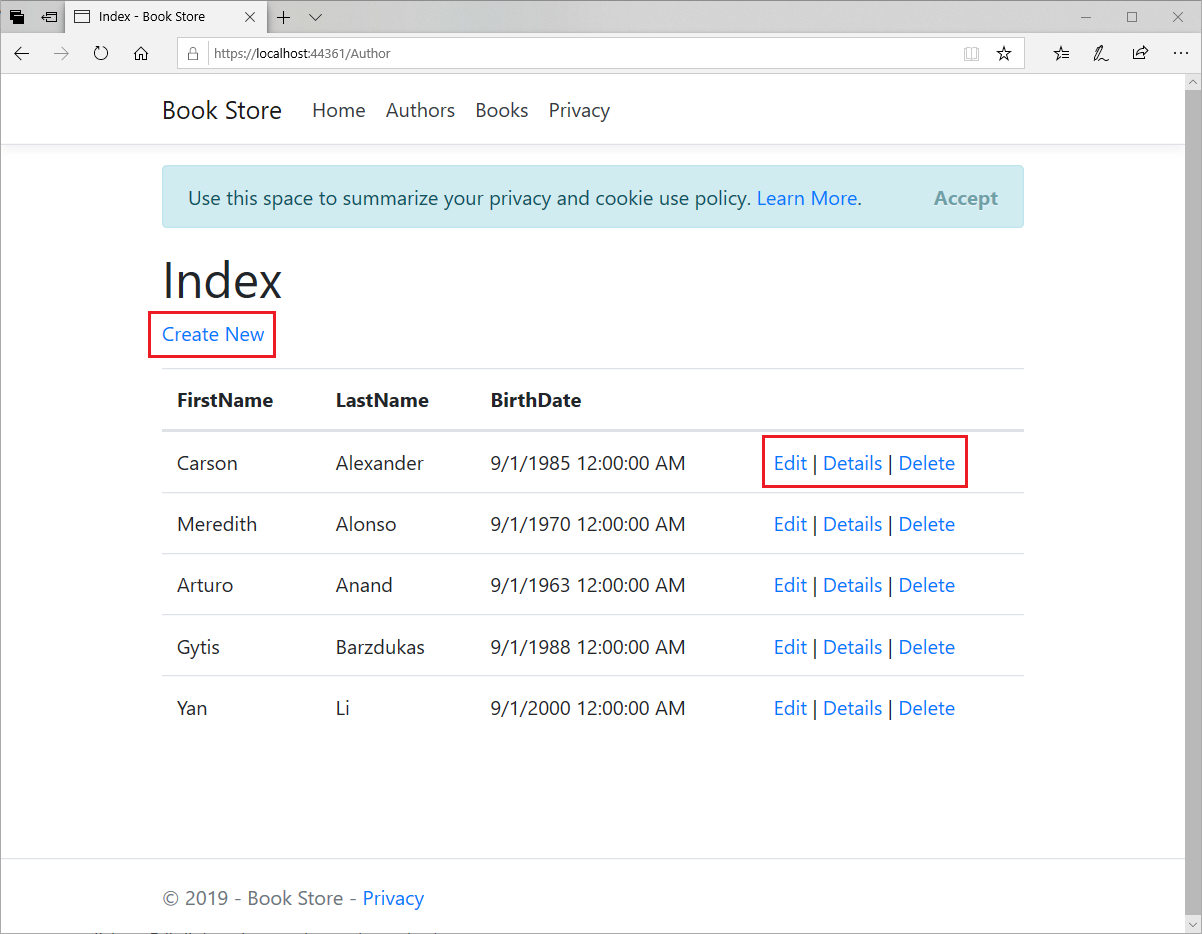
In Details method, the key value is passed to the method as the id parameter and comes from route data in the Details hyperlink on the Index page.
You can create a new author, delete or edit an author, and you can also see the details of any particular author using the highlighted links. Let's click on Edit link and you only see the author's name.
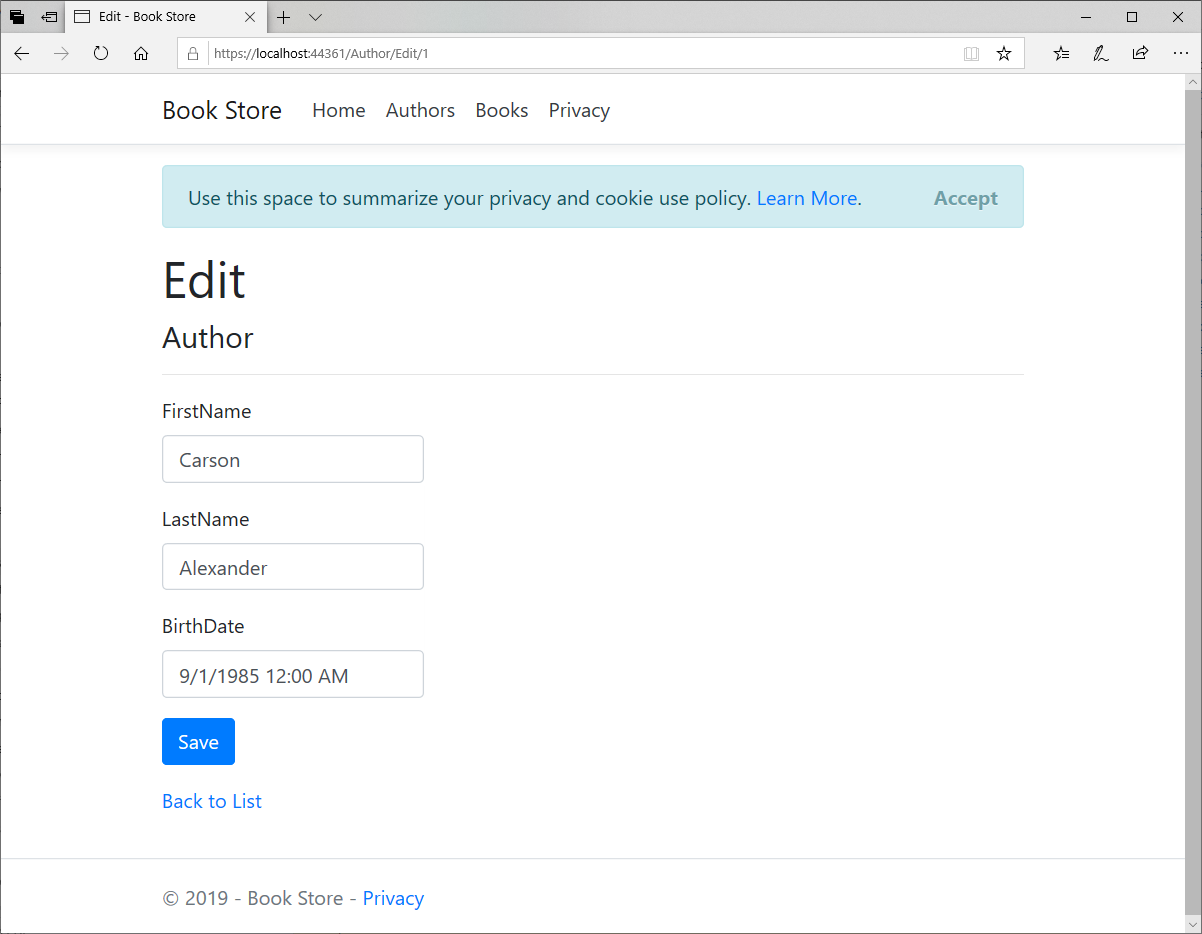
Details View
If you open the AuthorController you will see Details action method, the action method for the Details view uses the FirstOrDefaultAsync method to retrieve a single Author entity. Add code that calls the Include method which causes the context to load the Author.Books navigation property.
// GET: Author/Details/5
public async Task<IActionResult> Details(int? id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
var author = await _context.Authors
.Include(b => b.Books)
.FirstOrDefaultAsync(m => m.AuthorId == id);
if (author == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return View(author);
}
The scaffolded code for the author Details page left out the Books property because that property holds a collection and this is not displayed on the Details.cshtml file.
@model MvcWithEFCoreDemo.Models.Author
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Details";
}
<h1>Details</h1>
<div>
<h4>Author</h4>
<hr />
<dl class="row">
<dt class = "col-sm-2">
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.FirstName)
</dt>
<dd class = "col-sm-10">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.FirstName)
</dd>
<dt class = "col-sm-2">
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.LastName)
</dt>
<dd class = "col-sm-10">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.LastName)
</dd>
<dt class = "col-sm-2">
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.BirthDate)
</dt>
<dd class = "col-sm-10">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.BirthDate)
</dd>
</dl>
</div>
<div>
<a asp-action="Edit" asp-route-id="@Model.AuthorId">Edit</a> |
<a asp-action="Index">Back to List</a>
</div>
Each field is displayed using a DisplayFor helper, so here we will display the contents of the collection in an HTML table as shown below.
@model MvcWithEFCoreDemo.Models.Author
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Details";
}
<h1>Details</h1>
<div>
<h4>Author</h4>
<hr />
<dl class="row">
<dt class="col-sm-2">
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.FirstName)
</dt>
<dd class="col-sm-10">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.FirstName)
</dd>
<dt class="col-sm-2">
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.LastName)
</dt>
<dd class="col-sm-10">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.LastName)
</dd>
<dt class="col-sm-2">
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.BirthDate)
</dt>
<dd class="col-sm-10">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.BirthDate)
</dd>
<dt>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Books)
</dt>
<dd>
<table class="table">
<tr>
<th>Book Title</th>
</tr>
@foreach (var item in Model.Books)
{
<tr>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Title)
</td>
</tr>
}
</table>
</dd>
</dl>
</div>
<div>
<a asp-action="Edit" asp-route-id="@Model.AuthorId">Edit</a> |
<a asp-action="Index">Back to List</a>
</div>
Now run your application and go to the details page.
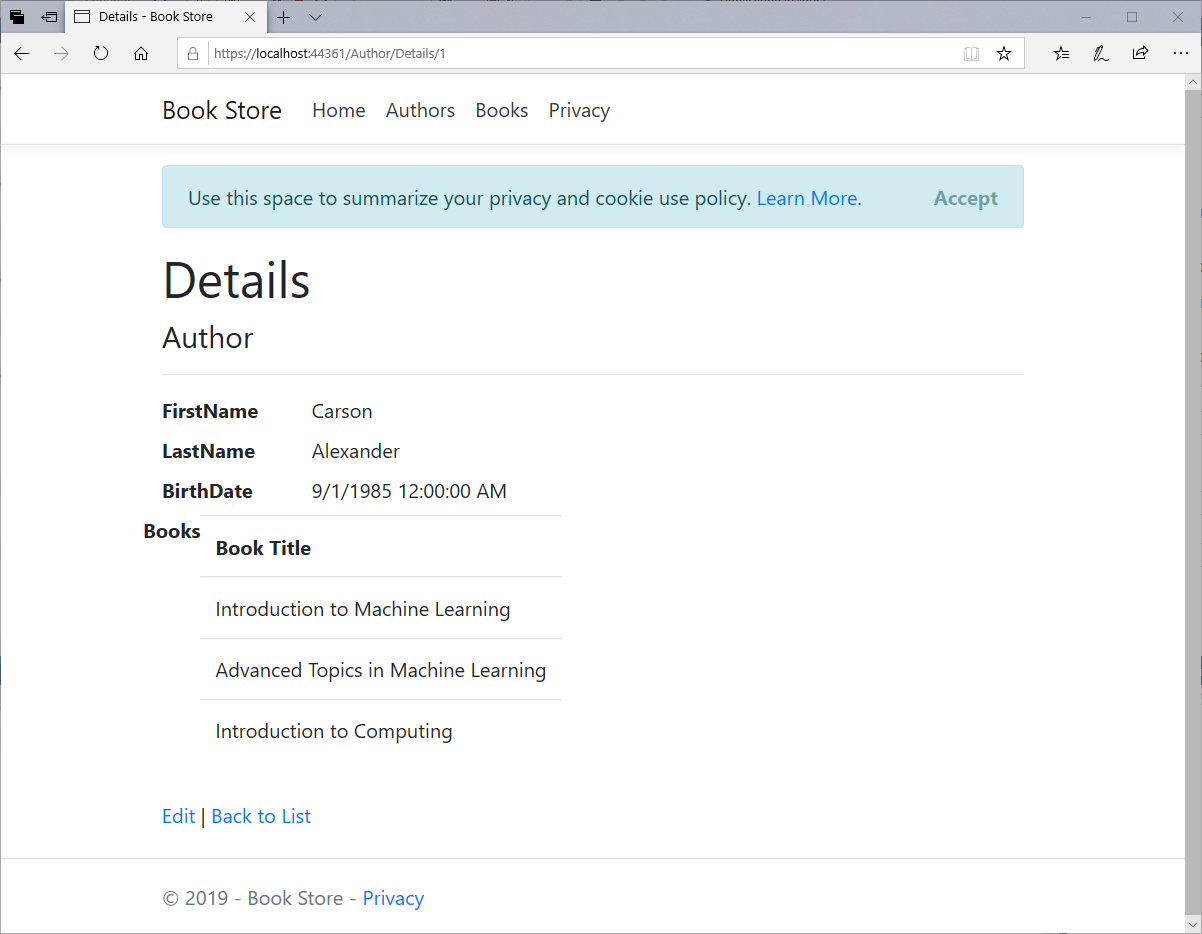
Create View
In AuthorController, you will see the Create action method. The following code shows the model validation check in the Create method.
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<IActionResult> Create([Bind("AuthorId,FirstName,LastName,BirthDate")] Author author)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
_context.Add(author);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
return View(author);
}
- This code adds the
Authorentity created by the ASP.NET MVC model binder to theAuthorsentity set and then saves the changes to the database. - Model binder refers to the ASP.NET MVC functionality that makes it easier for you to work with data submitted by a form.
- A model binder converts posted form values to CLR types and passes them to the action method in parameters.
- In this case, the model binder instantiates an
Authorentity for you using property values from the Form collection.
Let's update the Create action method adding a try-catch block and remove ID from the Bind attribute.
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult Create([Bind(Include = "FirstName,LastName,BirthDate")] Author author)
{
try
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
db.Authors.Add(author);
db.SaveChanges();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
}
catch (DbUpdateException /* ex */)
{
//Log the error (uncomment ex variable name and write a log.
ModelState.AddModelError("", "Unable to save changes. " +
"Try again, and if the problem persists " +
"see your system administrator.");
}
return View(author);
}
The code in Views\Author\Create.cshtml is as follows.
@model MvcWithEFCoreDemo.Models.Author
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Create";
}
<h1>Create</h1>
<h4>Author</h4>
<hr />
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">
<form asp-action="Create">
<div asp-validation-summary="ModelOnly" class="text-danger"></div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="FirstName" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="FirstName" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="FirstName" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="LastName" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="LastName" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="LastName" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="BirthDate" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="BirthDate" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="BirthDate" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<input type="submit" value="Create" class="btn btn-primary" />
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
<div>
<a asp-action="Index">Back to List</a>
</div>
@section Scripts {
@{await Html.RenderPartialAsync("_ValidationScriptsPartial");}
}
It uses labels, input, and span (for validation messages), tag helpers, for each field. This is server-side validation that you get by default; in a later tutorial, you'll see how to add attributes that will generate code for client-side validation also.
Edit View
The HttpGet Edit method (the one without the HttpPost attribute) retrieves the selected Author entity, as you saw in the Details method. You don't need to change this method. In the HttpPost Edit, the scaffolder generated a Bind attribute and added the entity created by the model binder to the entity set with a Modified flag. That code isn't recommended for many scenarios because the Bind attribute clears out any pre-existing data in fields not listed in the Include. parameter. So let's replace the HttpPost Edit action method with the following code.
[HttpPost, ActionName("Edit")]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<IActionResult> EditPost(int? id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
var authorToUpdate = await _context.Authors.FirstOrDefaultAsync(s => s.AuthorId == id);
if (await TryUpdateModelAsync<Author>(
authorToUpdate,
"",
s => s.FirstName, s => s.LastName, s => s.BirthDate))
{
try
{
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
catch (DbUpdateException /* ex */)
{
//Log the error (uncomment ex variable name and write a log.)
ModelState.AddModelError("", "Unable to save changes. " +
"Try again, and if the problem persists, " +
"see your system administrator.");
}
}
return View(authorToUpdate);
}
These changes implement a security best practice to prevent overposting.
- To prevent overposting, the fields that you want to be updateable by the Edit page are whitelisted in the
TryUpdateModelparameters. - The Entity Framework's automatic change tracking sets the
EntityState.Modifiedflag on the entity. - When the
SaveChangesmethod is called, theModifiedflag causes EF to create SQL statements to update the database row. - As a result of these changes, the method signature of the
HttpPostEdit method is the same as theHttpGetEdit method; therefore we have renamed the method toEditPost. - The HTML and Razor code in
Views\Author\Edit.cshtmlis similar to what you saw inCreate.cshtml, and no changes are required.
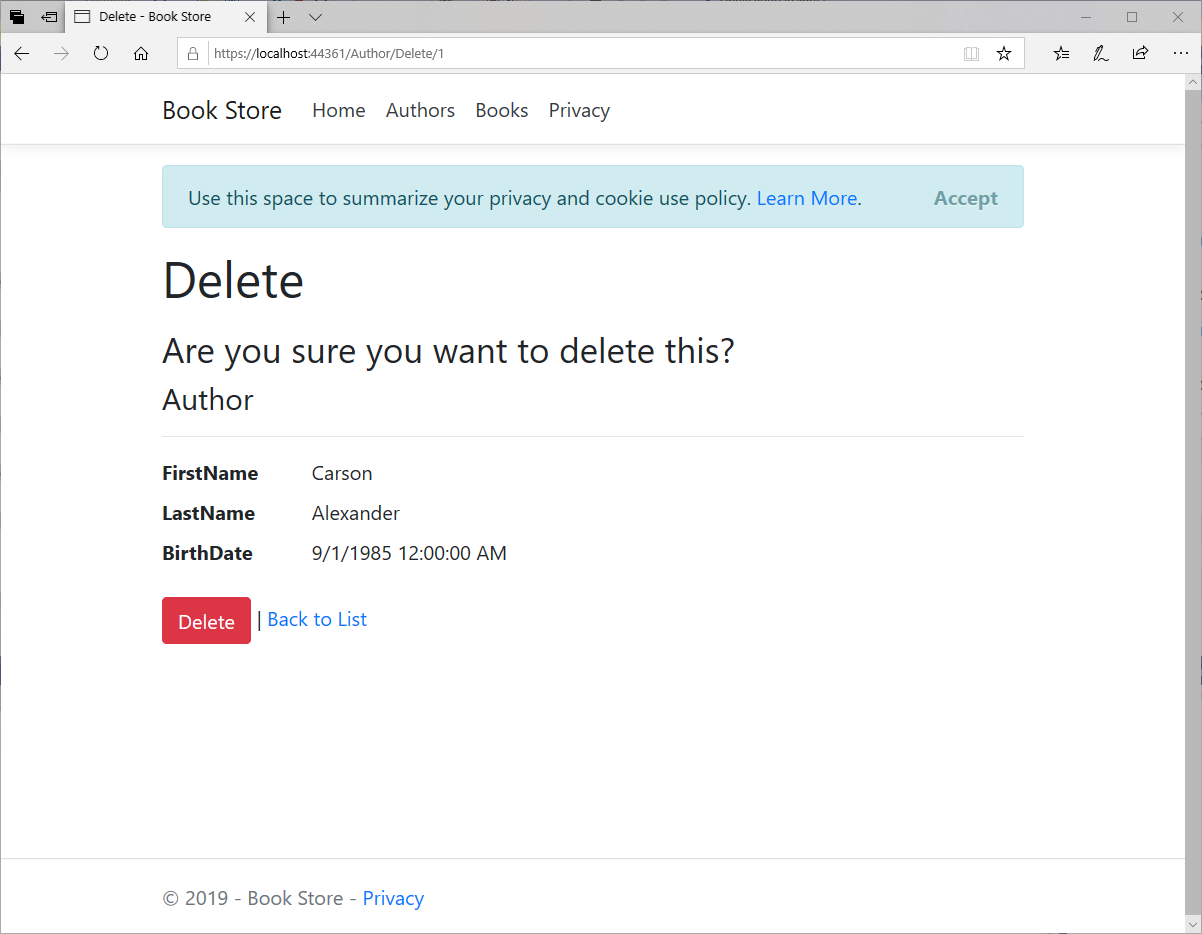
Delete View
In Controllers\AuthorController.cs, the template code for the HttpGet Delete method uses the FirstOrDefaultAsync method to retrieve the selected Author entity, as we saw in the Details and Edit methods. However, to implement a custom error message when the call to SaveChanges fails, we will add some functionality to this method and its corresponding view.
Let's replace the HttpGet Delete action method with the following code, which manages error reporting.
// GET: Author/Delete/5
public async Task<IActionResult> Delete(int? id, bool? saveChangesError = false)
{
if (id == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
var author = await _context.Authors
.AsNoTracking()
.FirstOrDefaultAsync(m => m.AuthorId == id);
if (author == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
if (saveChangesError.GetValueOrDefault())
{
ViewData["ErrorMessage"] =
"Delete failed. Try again, and if the problem persists " +
"see your system administrator.";
}
return View(author);
}
The method that is called in response to a GET request displays a view that gives the user a chance to approve or cancel the delete operation.
Replace the HttpPost Delete action method (named DeleteConfirmed) with the following code, which performs the actual delete operation and catches any database update errors.
[HttpPost, ActionName("Delete")]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<IActionResult> DeleteConfirmed(int id)
{
var author = await _context.Authors.FindAsync(id);
if (author == null)
{
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
try
{
_context.Authors.Remove(author);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
catch (DbUpdateException /* ex */)
{
//Log the error (uncomment ex variable name and write a log.)
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Delete), new { id = id, saveChangesError = true });
}
}
- It retrieves the selected entity, then calls the
Removemethod to set the entity's status to Deleted. - When
SaveChangesis called, a SQLDELETEcommand is generated.
In Views\Author\Delete.cshtml, add an error message @ViewBag.ErrorMessage between the <h1> heading and the <h3> heading as shown below.
@model MvcWithEFCoreDemo.Models.Author
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Delete";
}
<h1>Delete</h1>
<p class="text-danger">@ViewData["ErrorMessage"]</p>
<h3>Are you sure you want to delete this?</h3>
<div>
<h4>Author</h4>
<hr />
<dl class="row">
<dt class = "col-sm-2">
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.FirstName)
</dt>
<dd class = "col-sm-10">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.FirstName)
</dd>
<dt class = "col-sm-2">
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.LastName)
</dt>
<dd class = "col-sm-10">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.LastName)
</dd>
<dt class = "col-sm-2">
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.BirthDate)
</dt>
<dd class = "col-sm-10">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.BirthDate)
</dd>
</dl>
<form asp-action="Delete">
<input type="hidden" asp-for="AuthorId" />
<input type="submit" value="Delete" class="btn btn-danger" /> |
<a asp-action="Index">Back to List</a>
</form>
</div>
Run the app, select the Authors tab, and click a Delete hyperlink.