EF Core with MVC Paging
In this article, we will add paging to the Authors index page. To add paging we will create a PaginatedList class that uses Skip and Take statements to filter data on the server instead of always retrieving all rows of the table.
In the project folder, create PaginatedList.cs, and then replace the template code with the following code.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MvcWithEFCoreDemo
{
public class PaginatedList<T> : List<T>
{
public int PageIndex { get; private set; }
public int TotalPages { get; private set; }
public PaginatedList(List<T> items, int count, int pageIndex, int pageSize)
{
PageIndex = pageIndex;
TotalPages = (int)Math.Ceiling(count / (double)pageSize);
this.AddRange(items);
}
public bool HasPreviousPage
{
get
{
return (PageIndex > 1);
}
}
public bool HasNextPage
{
get
{
return (PageIndex < TotalPages);
}
}
public static async Task<PaginatedList<T>> CreateAsync(IQueryable<T> source, int pageIndex, int pageSize)
{
var count = await source.CountAsync();
var items = await source.Skip((pageIndex - 1) * pageSize).Take(pageSize).ToListAsync();
return new PaginatedList<T>(items, count, pageIndex, pageSize);
}
}
}
- The
CreateAsyncmethod in this code takes page size and page number and applies the appropriateSkipandTakestatements to theIQueryable. - When
ToListAsyncis called on theIQueryable, it will return a List containing only the requested page. - The properties
HasPreviousPageandHasNextPagecan be used to enable or disable Previous and Next paging buttons. - A
CreateAsyncmethod is used instead of a constructor to create thePaginatedList<T>object because constructors can't run asynchronous code.
Update Index Action
In Controllers\AuthorController.cs, replace the Index method with the following code.
public async Task<IActionResult> Index(string sortOrder, string currentFilter, string searchString, int? pageNumber)
{
ViewData["FirstNameSortParm"] = sortOrder == "first_name" ? "first_name_desc" : "first_name";
ViewData["LastNameSortParm"] = sortOrder == "last_name" ? "last_name_desc" : "last_name";
ViewData["BirthDateSortParm"] = sortOrder == "birth_date" ? "birth_date_desc" : "birth_date";
ViewData["CurrentSort"] = sortOrder;
if (searchString != null)
{
pageNumber = 1;
}
else
{
searchString = currentFilter;
}
ViewData["CurrentFilter"] = searchString;
var authors = _context.Authors.AsQueryable();
if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(searchString))
{
authors = authors.Where(a => a.LastName.Contains(searchString)
|| a.FirstName.Contains(searchString));
}
switch (sortOrder)
{
case "first_name_desc":
authors = authors.OrderByDescending(s => s.FirstName);
break;
case "first_name":
authors = authors.OrderBy(s => s.FirstName);
break;
case "last_name_desc":
authors = authors.OrderByDescending(s => s.LastName);
break;
case "last_name":
authors = authors.OrderBy(s => s.LastName);
break;
case "birth_date":
authors = authors.OrderBy(s => s.BirthDate);
break;
case "birth_date_desc":
authors = authors.OrderByDescending(s => s.BirthDate);
break;
default:
authors = authors.OrderBy(s => s.LastName);
break;
}
int pageSize = 3;
return View(await PaginatedList<Author>.CreateAsync(authors.AsNoTracking(), pageNumber ?? 1, pageSize));
}
This code adds a page number parameter, a current sort order parameter, and a current filter parameter to the method signature.
public async Task<IActionResult> Index(string sortOrder, string currentFilter, string searchString, int? pageNumber)
The first time the page is displayed, or if the user hasn't clicked a paging or sorting link, all the parameters will be null. If a paging link is clicked, the page variable will contain the page number to display.
The ViewData element named CurrentSort provides the view with the current sort order because this must be included in the paging links in order to keep the sort order the same while paging.
The ViewData element named CurrentFilter provides the view with the current filter string. This value must be included in the paging links in order to maintain the filter settings during paging, and it must be restored to the text box when the page is redisplayed.
If the search string is changed during paging, the page has to be reset to 1, because the new filter can result in different data to display. The search string is changed when a value is entered in the text box and the Submit button is pressed. In that case, the searchString parameter isn't null.
if (searchString != null)
{
pageNumber = 1;
}
else
{
searchString = currentFilter;
}
At the end of the Index method, the PaginatedList.CreateAsync method converts the author query to a single page of authors in a collection type that supports paging. That single page of authors is then passed to the view.
return View(await PaginatedList<Author>.CreateAsync(authors.AsNoTracking(), pageNumber ?? 1, pageSize));
Update Index View
In Views\Author\Index.cshtml, replace the existing code with the following code.
@model PaginatedList<MvcWithEFCoreDemo.Models.Author>
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Index";
}
<h1>Index</h1>
<p>
<a asp-action="Create">Create New</a>
</p>
<form asp-action="Index" method="get">
<div class="form-actions no-color">
<p>
Find by name: <input type="text" name="SearchString" value="@ViewData["currentFilter"]" />
<input type="submit" value="Search" class="btn btn-default" /> |
<a asp-action="Index">Back to Full List</a>
</p>
</div>
</form>
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>
<a asp-action="Index" asp-route-sortOrder="@ViewData["FirstNameSortParm"]" asp-route-currentFilter="@ViewData["CurrentFilter"]">FirstName</a>
</th>
<th>
<a asp-action="Index" asp-route-sortOrder="@ViewData["LastNameSortParm"]" asp-route-currentFilter="@ViewData["CurrentFilter"]">LastName</a>
</th>
<th>
<a asp-action="Index" asp-route-sortOrder="@ViewData["BirthDateSortParm"]" asp-route-currentFilter="@ViewData["CurrentFilter"]">BirthDate</a>
</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var item in Model)
{
<tr>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.FirstName)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.LastName)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.BirthDate)
</td>
<td>
<a asp-action="Edit" asp-route-id="@item.AuthorId">Edit</a> |
<a asp-action="Details" asp-route-id="@item.AuthorId">Details</a> |
<a asp-action="Delete" asp-route-id="@item.AuthorId">Delete</a>
</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
@{
var prevDisabled = !Model.HasPreviousPage ? "disabled" : "";
var nextDisabled = !Model.HasNextPage ? "disabled" : "";
}
<a asp-action="Index"
asp-route-sortOrder="@ViewData["CurrentSort"]"
asp-route-pageNumber="@(Model.PageIndex - 1)"
asp-route-currentFilter="@ViewData["CurrentFilter"]"
class="btn btn-default @prevDisabled">
Previous
</a>
<a asp-action="Index"
asp-route-sortOrder="@ViewData["CurrentSort"]"
asp-route-pageNumber="@(Model.PageIndex + 1)"
asp-route-currentFilter="@ViewData["CurrentFilter"]"
class="btn btn-default @nextDisabled">
Next
</a>
The @model statement at the top of the page specifies that the view now gets a PaginatedList<T> object instead of a <T> object.
The column header links use the query string to pass the current search string to the controller so that the user can sort within filter results:
<a asp-action="Index" asp-route-sortOrder="@ViewData["FirstNameSortParm"]" asp-route-currentFilter="@ViewData["CurrentFilter"]">FirstName</a>
The paging buttons are displayed by tag helpers.
<a asp-action="Index"
asp-route-sortOrder="@ViewData["CurrentSort"]"
asp-route-pageNumber="@(Model.PageIndex - 1)"
asp-route-currentFilter="@ViewData["CurrentFilter"]"
class="btn btn-default @prevDisabled">
Previous
</a>
Let's run your application and you will see pagination on the Author index page.
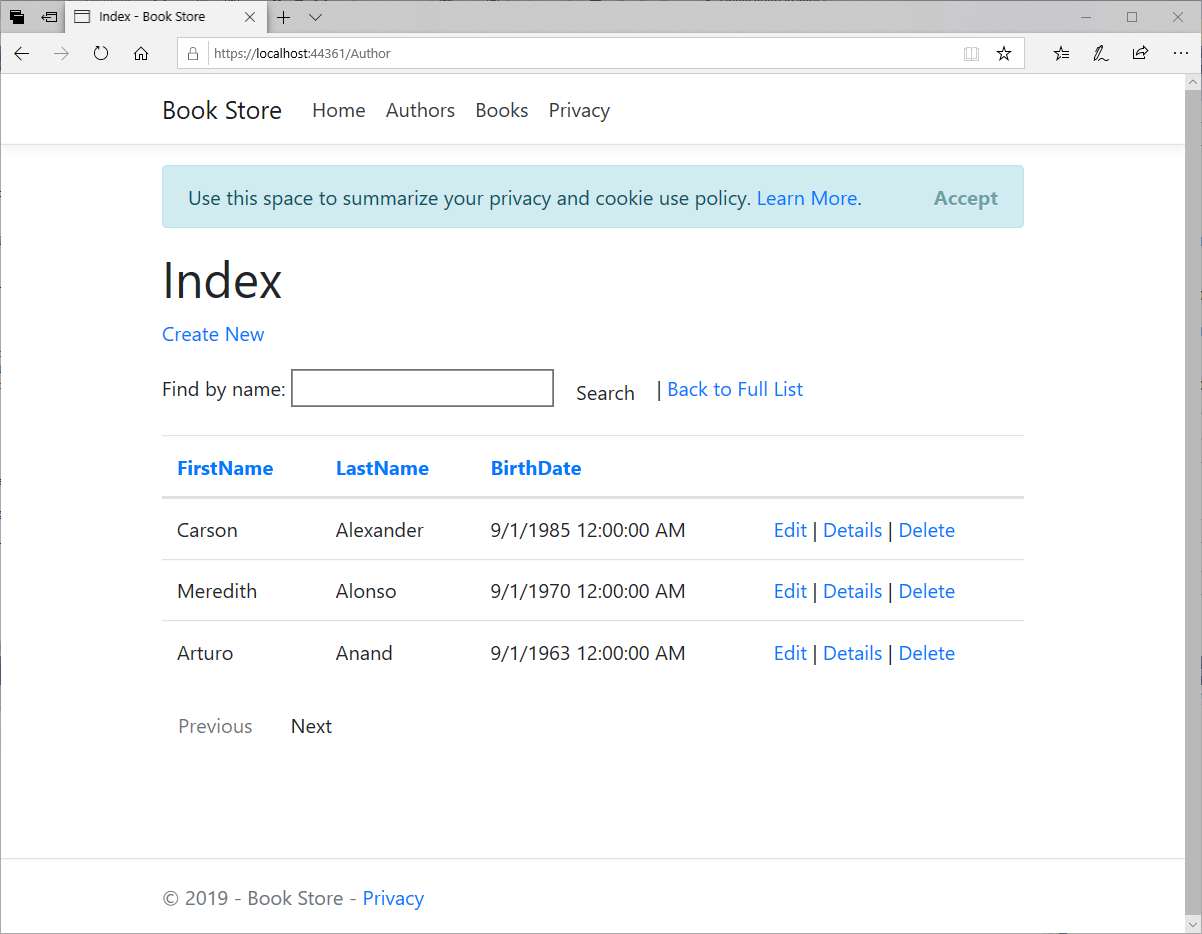
Click the paging links to make sure paging works.
