EF 6 + MVC MVC Life Cycle
A life cycle is a series of steps or events used to handle some type of request or to change an application state.
- You may already be familiar with various framework life cycles, the concept is not unique to MVC.
- To gain full control over the developer platform, you must understand the life cycle of ASP.NET MVC.
MVC has two life cycles
- Application life cycle
- Request life cycle
Application Life Cycle
- The application life cycle is the time at which the application process actually begins running IIS until the time it stops.
- This is marked by the application start and end events in the startup file of your application.
Request life Cycle
When the user sends request from the browser, it's been handled by Routing concept and which navigates it to the appropriate Controller where controller picks up the relevant View and send it as a response to the User.
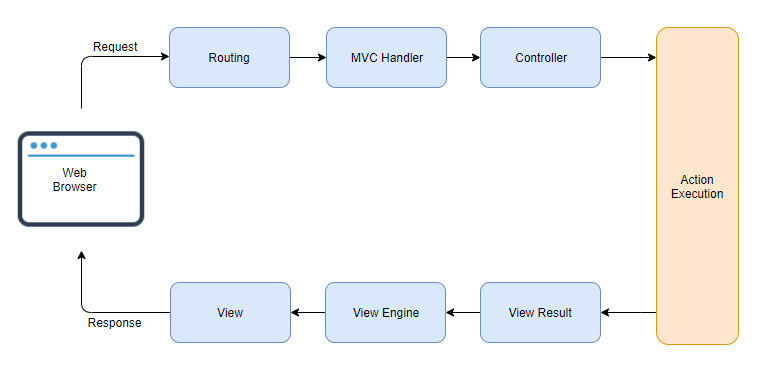
- The entry point for every MVC application begins with routing. After the ASP.NET platform has received a request, it figures out how it should be handled through the URL Routing Module.
- The MVC framework handles converting the route data into a concrete controller that can handle requests.
- When the controller is created, the Controller's ActionInvoker determines which specific action to invoke on the controller.
- The action method receives user input, prepares the appropriate response data, and then executes the result by returning a result type.
- The first step in the execution of the View Result involves the selection of the appropriate View Engine to render the View Result.
- Action method may return a text string, a binary file or a JSON formatted data. The most important Action Result is the ViewResult, which renders and returns an HTML page to the browser by using the current view engine.
