EF 6 + MVC Command Interception
The high-level goal for the interception feature is to allow external code to observe and potentially intercept EF operations.
- Anytime Entity Framework sends a command to the database this command can be intercepted by application code.
- Using this approach you can capture a lot more information transiently without having to untidy your code.
- EF6 provides a dedicated logging API that can make it easier to do logging.
- In this article, we will cover how to use the Entity Framework's interception feature directly for logging.
Create Logging Interface
Let's create a folder and call it Logging and then create a class file named ILogger.cs, and replace the following code.
using System;
namespace MvcWithEF6Demo.Logging
{
public interface ILogger
{
void Information(string message);
void Information(string fmt, params object[] vars);
void Information(Exception exception, string fmt, params object[] vars);
void Warning(string message);
void Warning(string fmt, params object[] vars);
void Warning(Exception exception, string fmt, params object[] vars);
void Error(string message);
void Error(string fmt, params object[] vars);
void Error(Exception exception, string fmt, params object[] vars);
void TraceApi(string componentName, string method, TimeSpan timespan);
void TraceApi(string componentName, string method, TimeSpan timespan, string properties);
void TraceApi(string componentName, string method, TimeSpan timespan, string fmt, params object[] vars);
}
}
The interface provides three tracing levels to indicate the relative importance of logs, and one designed to provide latency information for external service calls such as database queries.
- The logging methods have overloads that let you pass in an exception.
- The exception information including stack trace and inner exceptions is logged by the class that implements the interface.
- The TraceApi methods enable you to track the latency of each call to an external service such as SQL Database.
Implement Logging Interface
In the Logging folder, create a class file named Logger.cs, which will implement the ILogger interface as shown below.
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Text;
namespace MvcWithEF6Demo.Logging
{
public class Logger : ILogger
{
public void Information(string message)
{
Trace.TraceInformation(message);
}
public void Information(string fmt, params object[] vars)
{
Trace.TraceInformation(fmt, vars);
}
public void Information(Exception exception, string fmt, params object[] vars)
{
Trace.TraceInformation(FormatExceptionMessage(exception, fmt, vars));
}
public void Warning(string message)
{
Trace.TraceWarning(message);
}
public void Warning(string fmt, params object[] vars)
{
Trace.TraceWarning(fmt, vars);
}
public void Warning(Exception exception, string fmt, params object[] vars)
{
Trace.TraceWarning(FormatExceptionMessage(exception, fmt, vars));
}
public void Error(string message)
{
Trace.TraceError(message);
}
public void Error(string fmt, params object[] vars)
{
Trace.TraceError(fmt, vars);
}
public void Error(Exception exception, string fmt, params object[] vars)
{
Trace.TraceError(FormatExceptionMessage(exception, fmt, vars));
}
public void TraceApi(string componentName, string method, TimeSpan timespan)
{
TraceApi(componentName, method, timespan, "");
}
public void TraceApi(string componentName, string method, TimeSpan timespan, string fmt, params object[] vars)
{
TraceApi(componentName, method, timespan, string.Format(fmt, vars));
}
public void TraceApi(string componentName, string method, TimeSpan timespan, string properties)
{
string message = String.Concat("Component:", componentName, ";Method:", method, ";Timespan:", timespan.ToString(), ";Properties:", properties);
Trace.TraceInformation(message);
}
private static string FormatExceptionMessage(Exception exception, string fmt, object[] vars)
{
// Simple exception formatting: for a more comprehensive version see
// http://code.msdn.microsoft.com/windowsazure/Fix-It-app-for-Building-cdd80df4
var sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.Append(string.Format(fmt, vars));
sb.Append(" Exception: ");
sb.Append(exception.ToString());
return sb.ToString();
}
}
}
The implementation uses the System.Diagnostics to do the tracing. This is a built-in feature of .NET which makes it easy to generate and use tracing information.
Create Interceptor
To implement command interception, we need to create a custom interceptor and register it accordingly. Entity Framework will call into every time it is going to send a query to the database.
Let's create a new class BookStoreInterceptorLogging in the DAL folder that implements DbCommandInterceptor interface.
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Data.Common;
using System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.Interception;
using MvcWithEF6Demo.Logging;
namespace MvcWithEF6Demo.DAL
{
public class BookStoreInterceptorLogging : DbCommandInterceptor
{
private ILogger _logger = new Logger();
private readonly Stopwatch _stopwatch = new Stopwatch();
public override void ScalarExecuting(DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<object> interceptionContext)
{
base.ScalarExecuting(command, interceptionContext);
_stopwatch.Restart();
}
public override void ScalarExecuted(DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<object> interceptionContext)
{
_stopwatch.Stop();
if (interceptionContext.Exception != null)
{
_logger.Error(interceptionContext.Exception, "Error executing command: {0}", command.CommandText);
}
else
{
_logger.TraceApi("SQL Database", "BookStoreInterceptor.ScalarExecuted", _stopwatch.Elapsed, "Command: {0}: ", command.CommandText);
}
base.ScalarExecuted(command, interceptionContext);
}
public override void NonQueryExecuting(DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<int> interceptionContext)
{
base.NonQueryExecuting(command, interceptionContext);
_stopwatch.Restart();
}
public override void NonQueryExecuted(DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<int> interceptionContext)
{
_stopwatch.Stop();
if (interceptionContext.Exception != null)
{
_logger.Error(interceptionContext.Exception, "Error executing command: {0}", command.CommandText);
}
else
{
_logger.TraceApi("SQL Database", "BookStoreInterceptor.NonQueryExecuted", _stopwatch.Elapsed, "Command: {0}: ", command.CommandText);
}
base.NonQueryExecuted(command, interceptionContext);
}
public override void ReaderExecuting(DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<DbDataReader> interceptionContext)
{
base.ReaderExecuting(command, interceptionContext);
_stopwatch.Restart();
}
public override void ReaderExecuted(DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<DbDataReader> interceptionContext)
{
_stopwatch.Stop();
if (interceptionContext.Exception != null)
{
_logger.Error(interceptionContext.Exception, "Error executing command: {0}", command.CommandText);
}
else
{
_logger.TraceApi("SQL Database", "BookStoreInterceptor.ReaderExecuted", _stopwatch.Elapsed, "Command: {0}: ", command.CommandText);
}
base.ReaderExecuted(command, interceptionContext);
}
}
}
For successful queries or commands, this code writes an Information log with latency information. For exceptions, it creates an Error log.
Register Interceptor
Once a class that implements one or more of the interception interfaces has been created it can be registered with EF using the DbInterception class as shown below.
DbInterception.Add(new BookStoreInterceptorLogging());
In Global.asax, replace the following code.
using System.Web.Mvc;
using System.Web.Optimization;
using System.Web.Routing;
using MvcWithEF6Demo.DAL;
using System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.Interception;
namespace MvcWithEF6Demo
{
public class MvcApplication : System.Web.HttpApplication
{
protected void Application_Start()
{
AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas();
FilterConfig.RegisterGlobalFilters(GlobalFilters.Filters);
RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes);
BundleConfig.RegisterBundles(BundleTable.Bundles);
DbInterception.Add(new BookStoreInterceptorLogging());
}
}
}
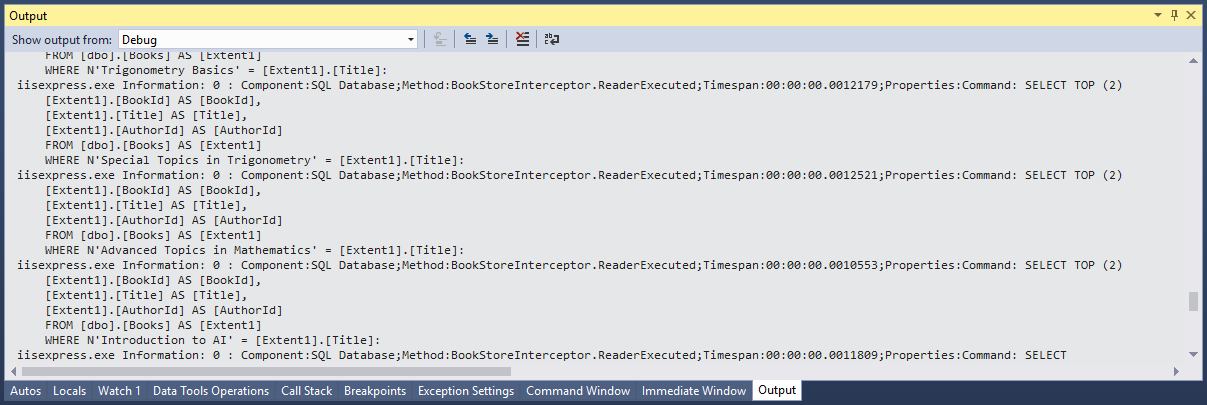
Let's run your application in debug mode, and then click the Authors tab. Now if you look at the Output window, you will see the tracing output.