EF 6 + MVC Use Asynchronous Code
So far we have used the synchronous programming model to read, write and update data. In this article, we will see how to implement the asynchronous programming model.
Why Asynchronous Programming?
A web server has a limited number of threads available, and in high load situations, all of the available threads might be in use. When that happens, the server can't process new requests until the threads are freed up.
- With synchronous code, many threads may be tied up while they aren't doing any work because they're waiting for I/O to complete.
- With asynchronous code, when a process is waiting for I/O to complete, its thread is freed up for the server to use for processing other requests.
- As a result, the asynchronous code enables server resources to be used more efficiently, and the server is enabled to handle more traffic without delays.
Benefits
- In earlier versions of .NET, writing and testing asynchronous code was complex, error-prone, and hard to debug.
- In .NET 4.5, writing, testing, and debugging asynchronous code is so much easier than you should generally write asynchronous code unless you have a reason not to.
- Asynchronous code does introduce a small amount of overhead, but for low traffic situations, the performance hit is negligible. For high traffic situations, potential performance improvement is substantial.
- Asynchronous code can help an application perform better because it makes better use of server resources.
Create Book Controller
Let's create a BookController the same way we created an AuthorController, except this time we will select the Use async controller actions check box.
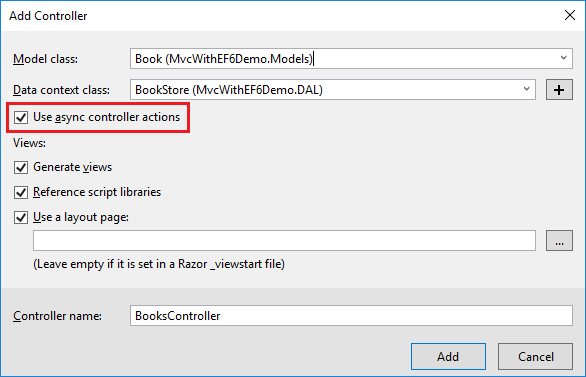
If you open the BookController and look at the Index action, you will see some changes as compared to synchronous code.
public async Task<ActionResult> Index()
{
var books = db.Books.Include(b => b.Author);
return View(await books.ToListAsync());
}
- The
asynckeyword tells the compiler to generate callbacks for parts of the method body and to automatically create theTask<ActionResult>object that is returned. - The return type was changed from
ActionResulttoTask<ActionResult>. TheTask<T>type represents ongoing work with a result of typeT. - The
awaitkeyword was applied to the web service call, when the compiler sees this keyword, behind the scenes it splits the method into two parts.- The first part ends with the operation that is started asynchronously.
- The second part is put into a callback method that is called when the operation completes.
- The asynchronous version of the ToList extension method was called.
ToListAsync
In Index method, you can see that books.ToList statement modified but not the var books = db.Books statement.
- It is because that only statements that cause queries or commands to be sent to the database are executed asynchronously.
- The
var books = db.Booksstatement sets up a query but the query is not executed until theToListmethod is called. - Therefore, only the
ToListmethod is executed asynchronously.
FindAsync
In the Details method and the HttpGet Edit and Delete methods, the Find method causes a query to be sent to the database, so that's the method that gets executed asynchronously.
public async Task<ActionResult> Delete(int? id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
Book book = await db.Books.FindAsync(id);
if (book == null)
{
return HttpNotFound();
}
return View(book);
}
SaveChangesAsync
In the Create, HttpPost Edit, and DeleteConfirmed methods, it is the SaveChanges method call that causes a command to be executed, not statements such as db.Books.Add(book) which only cause entities in memory to be modified.
public async Task<ActionResult> Create([Bind(Include = "BookId,Title,AuthorId")] Book book)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
db.Books.Add(book);
await db.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
ViewBag.AuthorId = new SelectList(db.Authors, "AuthorId", "FirstName", book.AuthorId);
return View(book);
}
Update Views
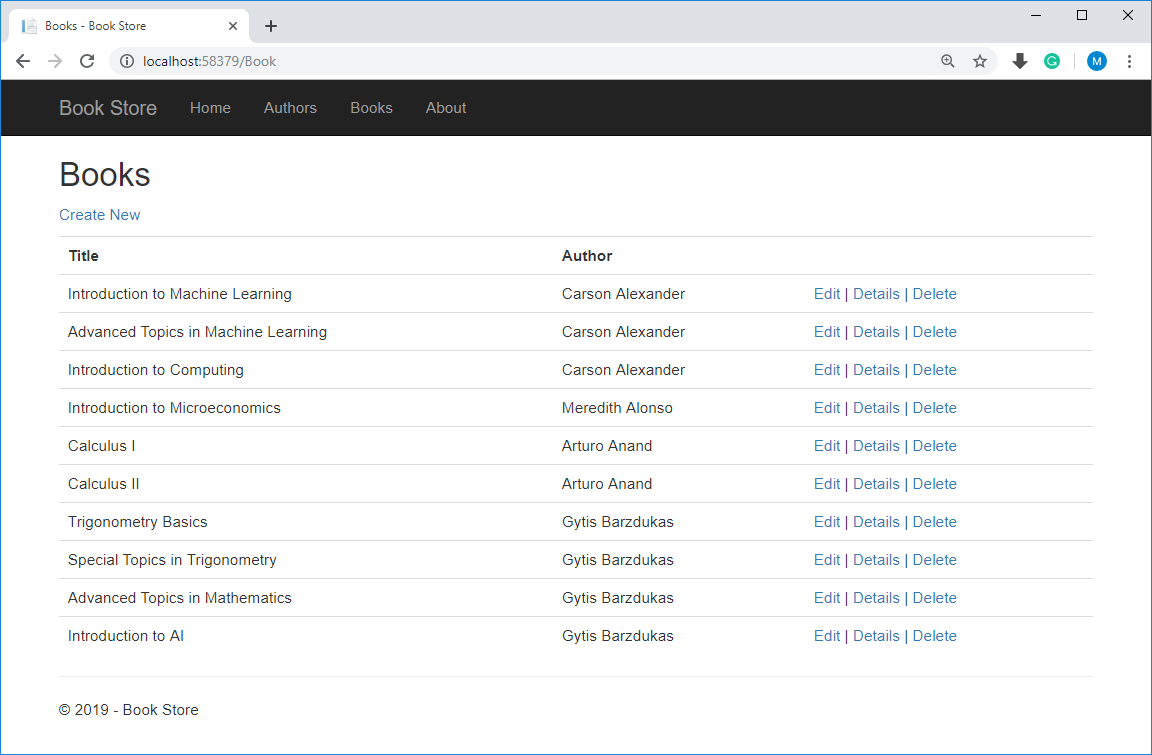
Let's replace the following code in Views\Book\Index.cshtml file by changing the title to Books, moves the Author name to the right, and provides the full name of the author.
@model IEnumerable<MvcWithEF6Demo.Models.Book>
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Books";
}
<h2>Books</h2>
<p>
@Html.ActionLink("Create New", "Create")
</p>
<table class="table">
<tr>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Title)
</th>
<th>
Author
</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
@foreach (var item in Model) {
<tr>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Title)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Author.FullName)
</td>
<td>
@Html.ActionLink("Edit", "Edit", new { id = item.BookId }) |
@Html.ActionLink("Details", "Details", new { id = item.BookId }) |
@Html.ActionLink("Delete", "Delete", new { id = item.BookId })
</td>
</tr>
}
</table>
In the Create, Delete, Details, and Edit views, we need to change the caption for the AuthorId field to Author.
In Create and Edit views you will see the caption line as shown below.
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.AuthorId, "AuthorId", htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
Replace the above line with the following line.
<label class="control-label col-md-2" for="AuthorId">Author</label>
Now let's update the Details view by using the author FullName instead of FirstName and also move the full name field below book title as shown below.
@model MvcWithEF6Demo.Models.Book
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Details";
}
<h2>Details</h2>
<div>
<h4>Book</h4>
<hr />
<dl class="dl-horizontal">
<dt>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Title)
</dt>
<dd>
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Title)
</dd>
<dt>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Author.FullName)
</dt>
<dd>
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Author.FullName)
</dd>
</dl>
</div>
<p>
@Html.ActionLink("Edit", "Edit", new { id = Model.BookId }) |
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index")
</p>
Repeat the same changes in Delete view as well.
@model MvcWithEF6Demo.Models.Book
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Delete";
}
<h2>Delete</h2>
<h3>Are you sure you want to delete this?</h3>
<div>
<h4>Book</h4>
<hr />
<dl class="dl-horizontal">
<dt>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Title)
</dt>
<dd>
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Title)
</dd>
<dt>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Author.FullName)
</dt>
<dd>
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Author.FullName)
</dd>
</dl>
@using (Html.BeginForm()) {
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<div class="form-actions no-color">
<input type="submit" value="Delete" class="btn btn-default" /> |
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index")
</div>
}
</div>
Now run your application and click on Books tab.