EF 6 + MVC Create Controller and Views
MVC controllers are responsible for responding to requests made against an ASP.NET MVC website. Each browser request is mapped to a particular controller.
For example, you entered the following URL into the address bar of your browser.
http://localhost/Author/Index/
In this case, a controller named AuthorController is invoked. The AuthorController is responsible for generating the response to the browser request.
- The controller decides which model will be selected, and then it takes the data from the model and passes the same to the respective view after that view is rendered.
- Actually, controllers are controlling the overall flow of the application taking the input and rendering the proper output.
To create a controller, right-click the Controllers folder in Solution Explorer, and select Add > New Scaffolded Item...
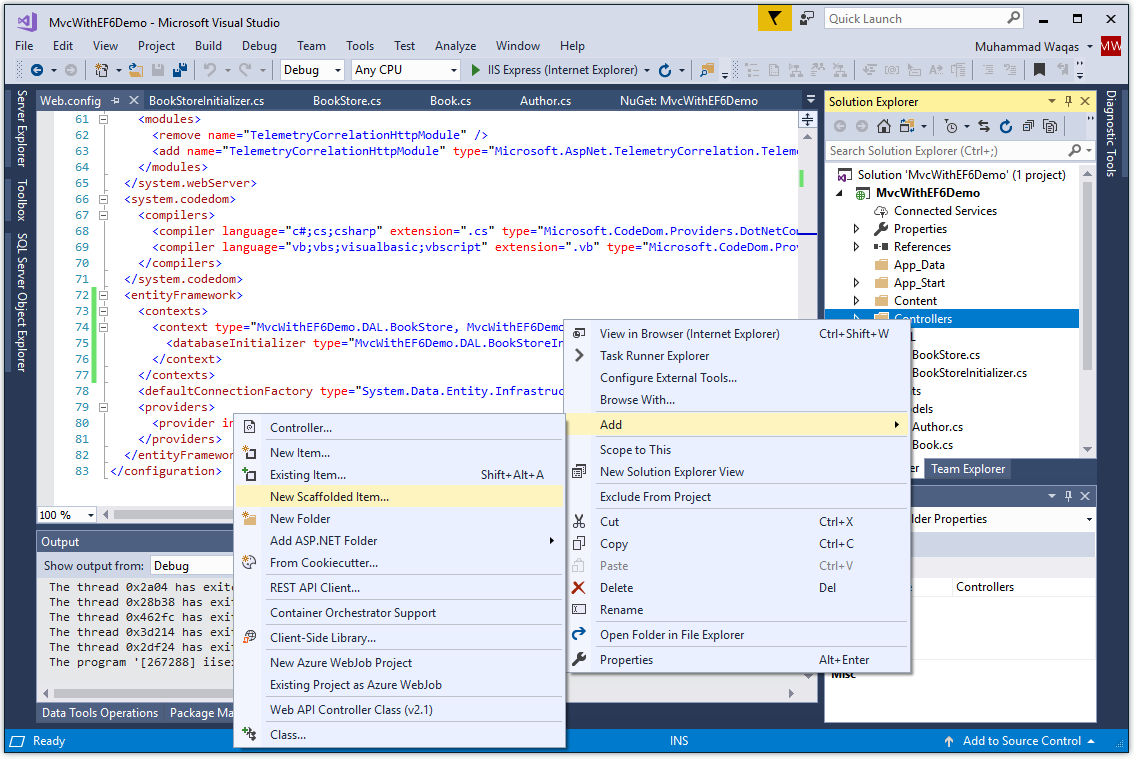
It will open the Add Scaffold dialog box.
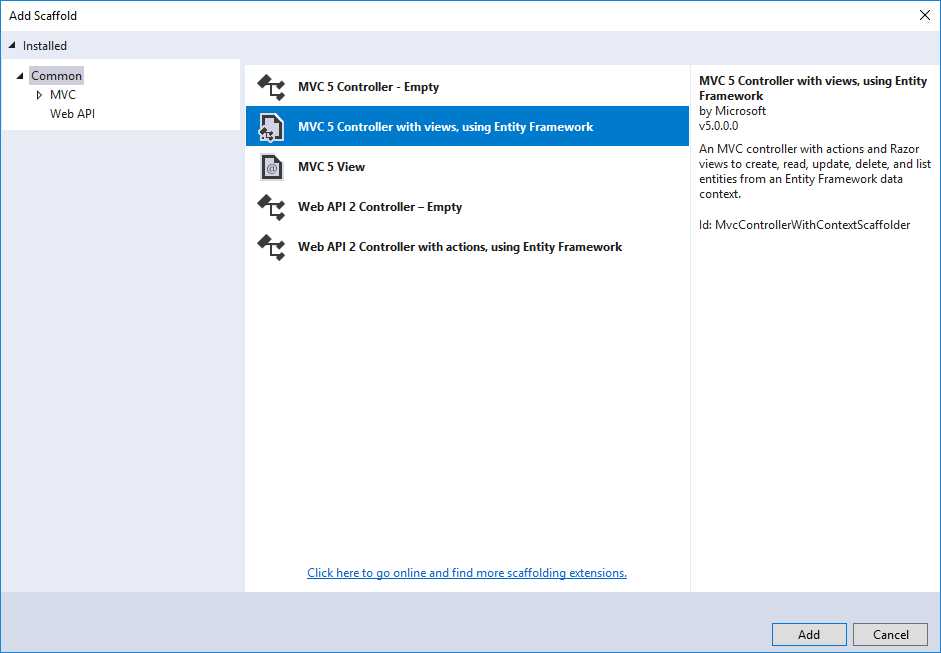
Select MVC 5 Controller with views, using Entity Framework, and then click Add button.
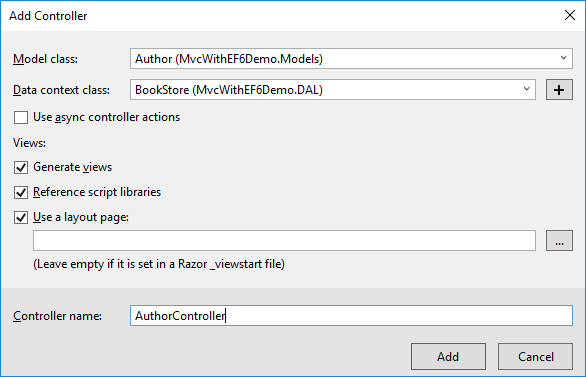
In the Add Controller dialog box, select Author (MvcWithEF6Demo.Models) from the Model class and BookStore (MvcWithEF6Demo.DAL) from the Data context class dropdown.
Enter AuthorController (not AuthorsController) as a Controller name and click Add button. The scaffolder creates an AuthorController.cs file and a set of views (.cshtml files) that work with the controller.
In the AuthorController.cs file, you will see that a class variable has been created that instantiates a database context object.
private BookStore db = new BookStore();
The Index action method gets a list of authors from the Authors table.
// GET: Author
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View(db.Authors.ToList());
}
Now if you open Views/Author/Index.cshtml file, you will see that the view displays the list of authors in a table.
@model IEnumerable<MvcWithEF6Demo.Models.Author>
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Index";
}
<h2>Index</h2>
<p>
@Html.ActionLink("Create New", "Create")
</p>
<table class="table">
<tr>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Name)
</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
@foreach (var item in Model)
{
<tr>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Name)
</td>
<td>
@Html.ActionLink("Edit", "Edit", new { id=item.AuthorId }) |
@Html.ActionLink("Details", "Details", new { id=item.AuthorId }) |
@Html.ActionLink("Delete", "Delete", new { id=item.AuthorId })
</td>
</tr>
}
</table>
Setup Menu Options
A few simple changes will set up the site menu, layout, and home page. Open Views\Shared_Layout.cshtml, and make the following changes.
- Change each occurrence of "My ASP.NET Application" and "Application name" to "Book Store".
- Add menu entries for Authors, and Books (controller and views will be added later), and delete the Contact entry.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>@ViewBag.Title - Book Store</title>
@Styles.Render("~/Content/css")
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/modernizr")
</head>
<body>
<div class="navbar navbar-inverse navbar-fixed-top">
<div class="container">
<div class="navbar-header">
<button type="button" class="navbar-toggle" data-toggle="collapse" data-target=".navbar-collapse">
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
</button>
@Html.ActionLink("Book Store", "Index", "Home", new { area = "" }, new { @class = "navbar-brand" })
</div>
<div class="navbar-collapse collapse">
<ul class="nav navbar-nav">
<li>@Html.ActionLink("Home", "Index", "Home")</li>
<li>@Html.ActionLink("Authors", "Index", "Author")</li>
<li>@Html.ActionLink("Books", "Index", "Book")</li>
<li>@Html.ActionLink("About", "About", "Home")</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="container body-content">
@RenderBody()
<hr />
<footer>
<p>© @DateTime.Now.Year - Book Store</p>
</footer>
</div>
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/jquery")
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/bootstrap")
@RenderSection("scripts", required: false)
</body>
</html>
Press Ctrl+F5 to run the project, click the Authors tab to see the test data that the Seed method inserted.
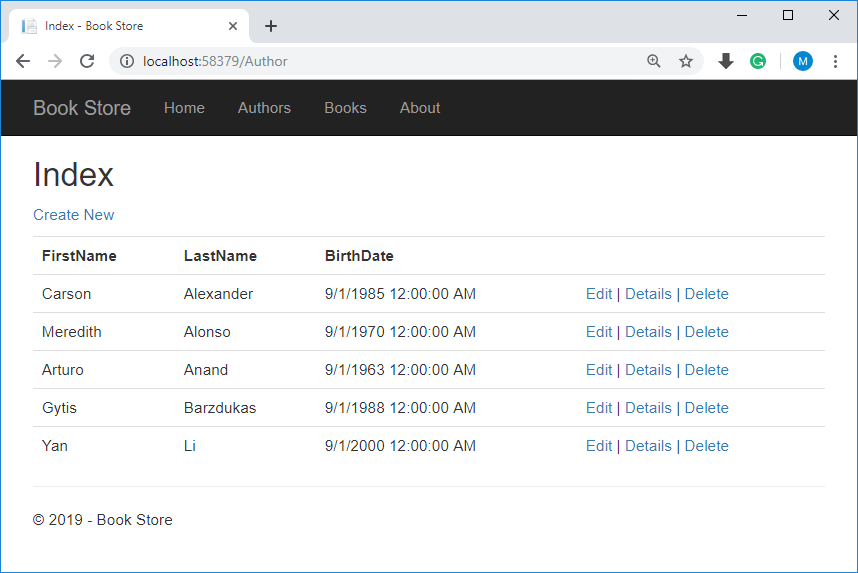
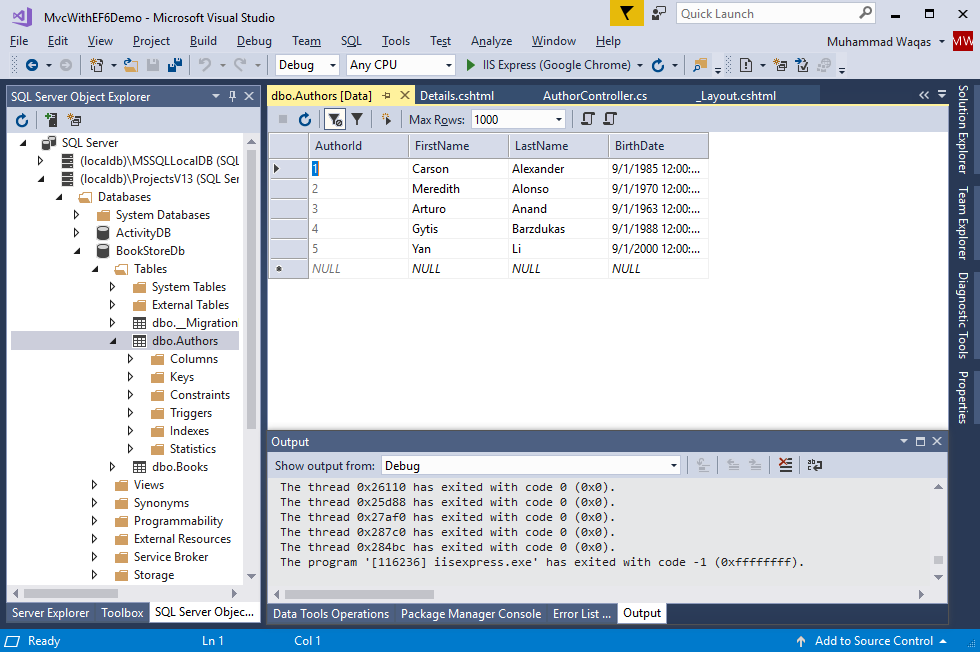
View Database
When you clicked on the Authors menu, then the application tried to access the database, EF discovered that there was no database, so EF then ran the seed method to populate the database with data.
You can use SQL Server Object Explorer to view the database in Visual Studio, by right-clicking on the Authors table and click View Data to see the rows that were inserted into the table.