Dapper + MVC Overview
What is MVC?
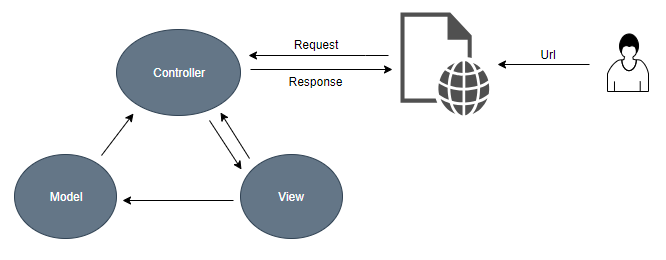
MVC stands for Model, View, and Controller. MVC separates the application into three components
- Model: Responsible for maintaining application data and business logic.
- View: The user interface of the application, which displays the data.
- Controller: Handles users' requests and renders appropriate View with Model data.
The MVC design pattern has been around for a few decades, and it's been used across many different technologies.
What is ASP.NET Core MVC?
The ASP.NET Core MVC framework is a lightweight, open-source, highly testable presentation framework optimized for ASP.NET Core.
- It provides a patterns-based way to build dynamic websites that enables a clean separation of concerns.
- It gives you full control over markup, supports TDD-friendly development, and uses the latest web standards.
Features
- Routing: A powerful URL-mapping component that lets you build applications that have comprehensible and searchable URLs.
- Model binding: Converts client request data into objects that the controller can handle.
- Model validation: Supports validation by decorating your model object with data annotation validation attributes.
- Dependency Injection (DI): Built-in support for dependency injection, controllers can request needed services through their constructors, allowing them to follow the Explicit Dependencies Principle.
- Filters: Encapsulate cross-cutting concerns, like exception handling or authorization.
- Areas: Provide a way to partition a large ASP.NET Core MVC Web app into smaller functional groupings.
- Web APIs: Support for building Web APIs, and you can build services that reach a broad range of clients, including browsers and mobile devices.
- Testability: The framework's use of interfaces and dependency injection make it well-suited to unit testing.
- Razor view engine: Razor is a compact, expressive, and fluid template markup language for defining views using embedded C# code.
- Strongly typed views: Razor views in MVC can be strongly typed based on your model.
- Tag Helpers: Enable server-side code to participate in creating and rendering HTML elements in Razor files.
- View Components: The
SetCompatibilityVersionmethod allows an app to opt-in or opt-out of potentially breaking behavior changes introduced in ASP.NET Core MVC 2.1 or later.
What is Dapper?
Dapper is a simple object mapper for .NET and owns the title of King of Micro ORM in terms of speed and is virtually as fast as using a raw ADO.NET data reader. An ORM is an Object Relational Mapper, which is responsible for mapping between database and programming language.
Dapper extends the IDbConnection by providing useful extension methods to query your database.
How Dapper Works?
It is a three-step process.
- Create an IDbConnection object.
- Write a query to perform CRUD operations.
- Pass query as a parameter in the Execute method.
