Dapper + MVC Create Controller
MVC controllers are responsible for responding to requests made against your website. Each browser request is mapped to a particular controller.
For example, you entered the following URL into the address bar of your browser.
http://localhost/Author/Index/
In this case, a controller named AuthorController is invoked. The AuthorController is responsible for generating the response to the browser request.
- The controller decides which model will be selected, and then it takes the data from the model and passes the same to the respective view after that view is rendered.
- Actually, controllers are controlling the overall flow of the application taking the input and rendering the proper output.
To create a controller, right-click the Controllers folder in Solution Explorer, and select Add > Controller...
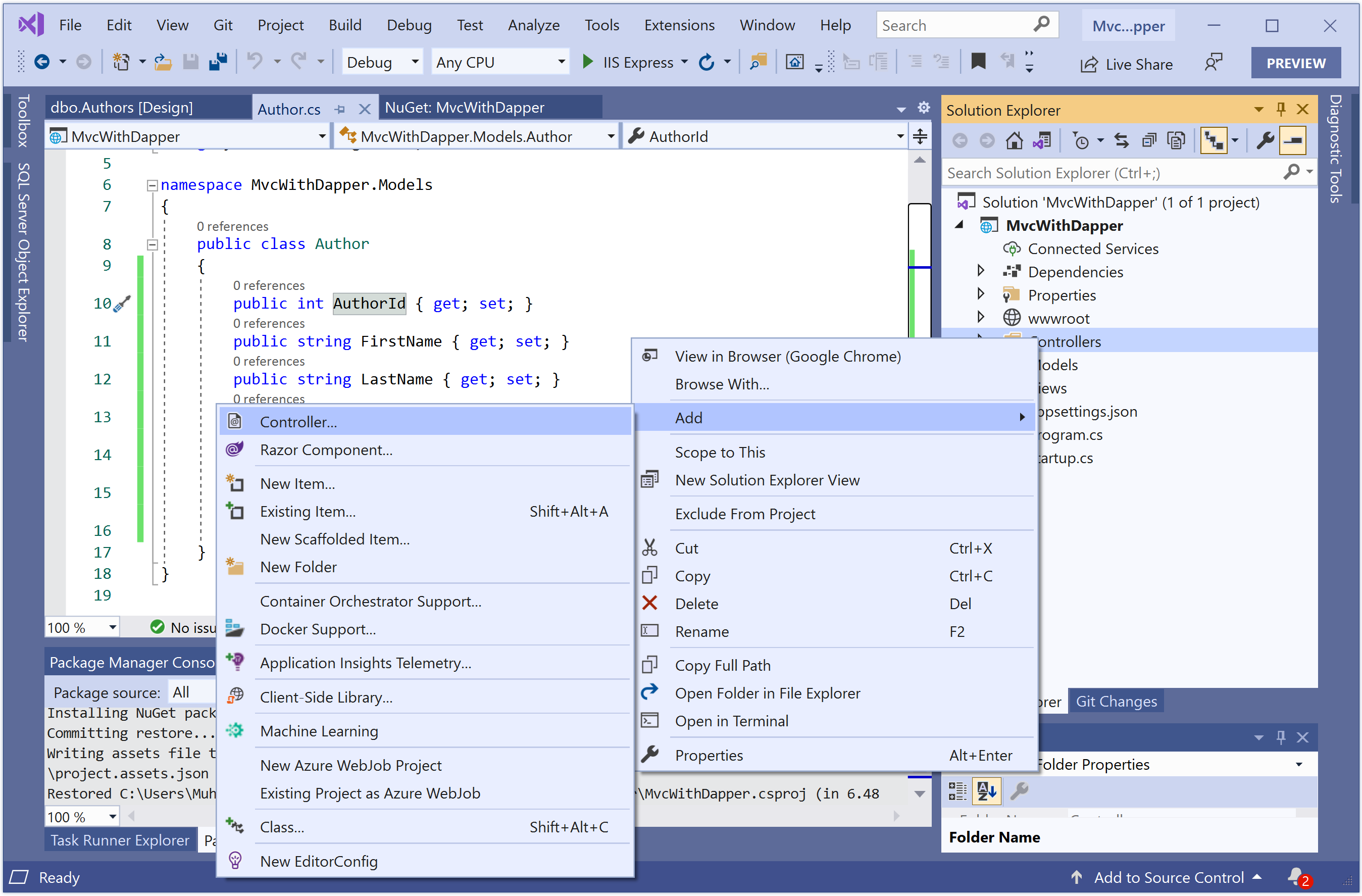
It will open the Add Scaffold dialog box.
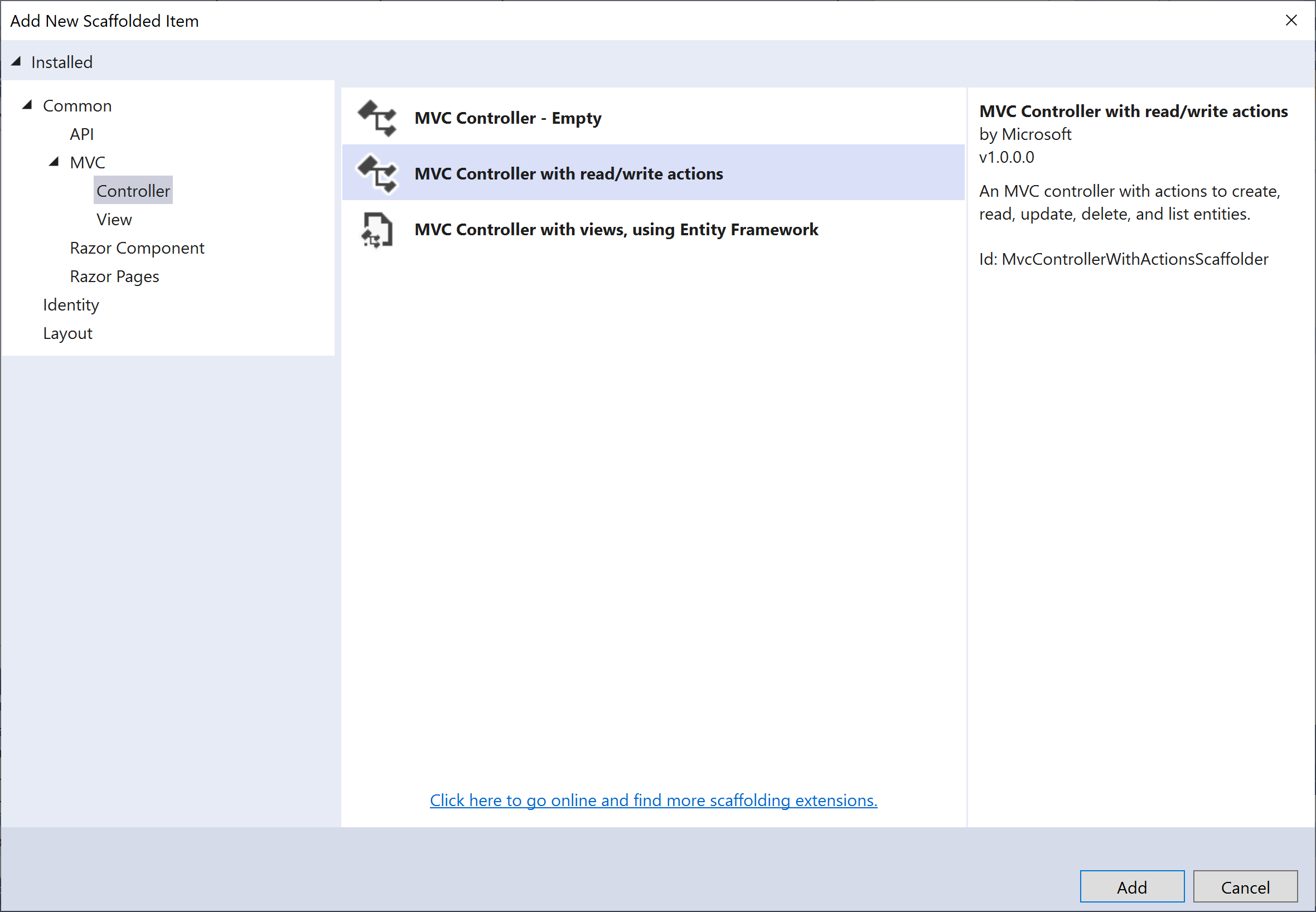
Select MVC controller with read/write actions, and then click Add button.
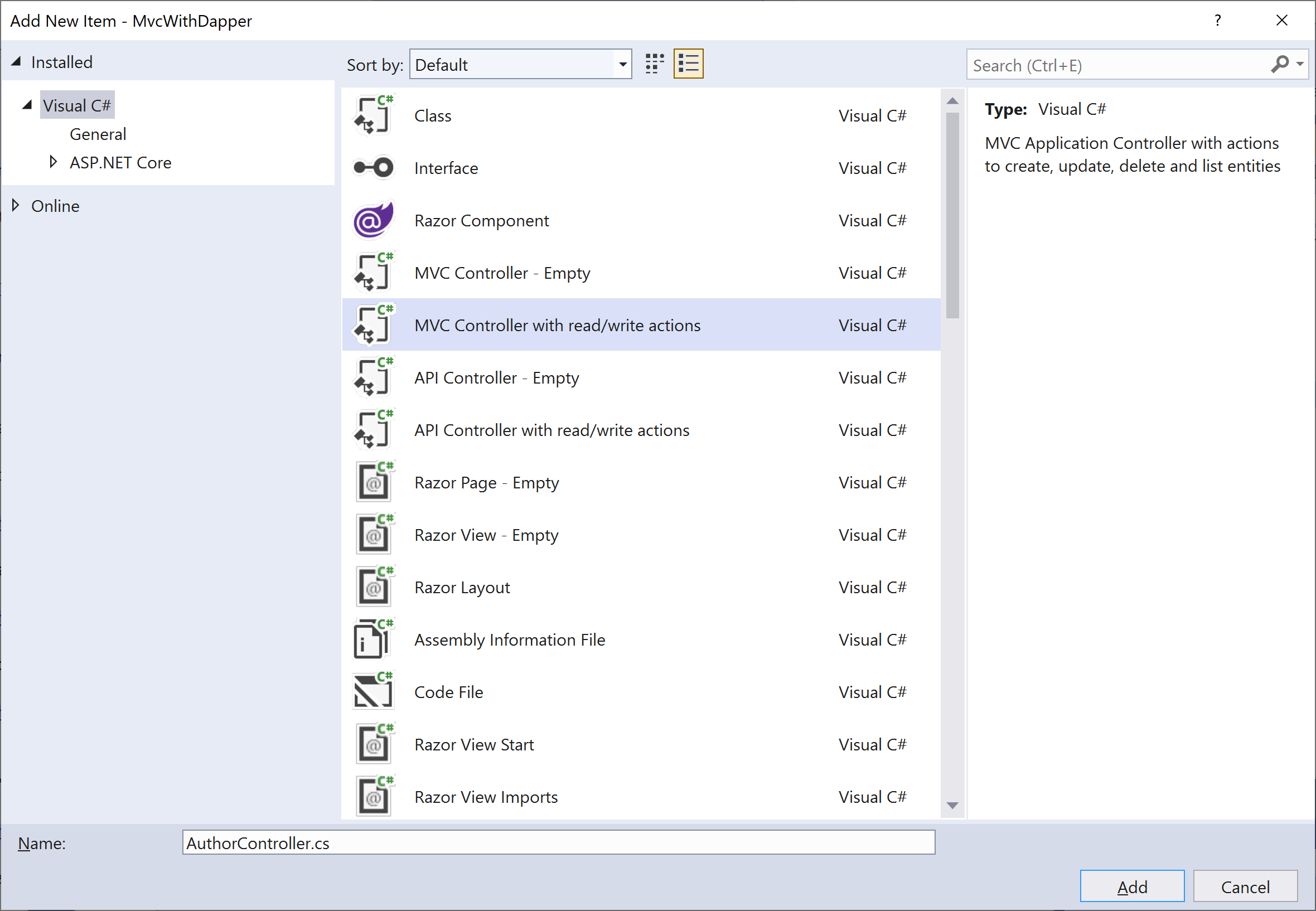
Enter AuthorController (not AuthorsController) as a Controller name and click Add button. The scaffolder creates an AuthorController.cs file.
In the AuthorController.cs file, you will see the following code.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MvcWithDapper.Controllers
{
public class AuthorController : Controller
{
// GET: AuthorController
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
// GET: AuthorController/Details/5
public ActionResult Details(int id)
{
return View();
}
// GET: AuthorController/Create
public ActionResult Create()
{
return View();
}
// POST: AuthorController/Create
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult Create(IFormCollection collection)
{
try
{
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
catch
{
return View();
}
}
// GET: AuthorController/Edit/5
public ActionResult Edit(int id)
{
return View();
}
// POST: AuthorController/Edit/5
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult Edit(int id, IFormCollection collection)
{
try
{
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
catch
{
return View();
}
}
// GET: AuthorController/Delete/5
public ActionResult Delete(int id)
{
return View();
}
// POST: AuthorController/Delete/5
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult Delete(int id, IFormCollection collection)
{
try
{
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
catch
{
return View();
}
}
}
}
