Dapper + MVC Create Data Model
Model is a collection of classes to interact with the database.
- A model stores data that is retrieved according to the commands from the Controller and displayed in the View.
- It can also be used to manipulate the data to implement the business logic.
To create a data model for our application, we will start with a simple Author entity.
Create Author Entity
In Solution Explorer, right-click on the Models folder and choose Add > Class. Enter a class file name Author.cs and add the following code.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MvcWithDapper.Models
{
public class Author
{
public int AuthorId { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string Address { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
public string PostalCode { get; set; }
public string Country { get; set; }
}
}
The AuthorId property will become the primary key column of the database table that corresponds to this class.
Create Database
To create the database, let's execute the following SQL statement.
CREATE DATABASE AuthorDb
It will create a database called AuthorDb. Now we need to add the Authors table by executing the following SQL statement.
USE [AuthorDb]
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Authors] (
[AuthorId] INT IDENTITY (1, 1) NOT NULL,
[FirstName] NVARCHAR (MAX) NULL,
[LastName] NVARCHAR (MAX) NULL,
[Address] NVARCHAR (MAX) NULL,
[City] NVARCHAR (MAX) NULL,
[PostalCode] NVARCHAR (MAX) NULL,
[Country] NVARCHAR (MAX) NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Authors] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED ([AuthorId] ASC)
);
Now you can see a database is created which contains an Authors table.
Initialize Database
To initialize the database with test data, execute the following SQL statement.
USE [AuthorDb]
GO
INSERT INTO Authors (FirstName, LastName, Address, City, PostalCode, Country) VALUES ('Karl', 'Jablonski', 'Skagen 21', 'Stavanger', '4006', 'Norway');
INSERT INTO Authors (FirstName, LastName, Address, City, PostalCode, Country) VALUES ('Matti', 'Karttunen', 'Keskuskatu 45', 'Helsinki', '21240', 'Finland');
INSERT INTO Authors (FirstName, LastName, Address, City, PostalCode, Country) VALUES ('Tom', 'Erichsen', '305 - 14th Ave. S. Suite 3B', 'Seattle', '98128', 'USA');
Now you will see the above-inserted records in the database.
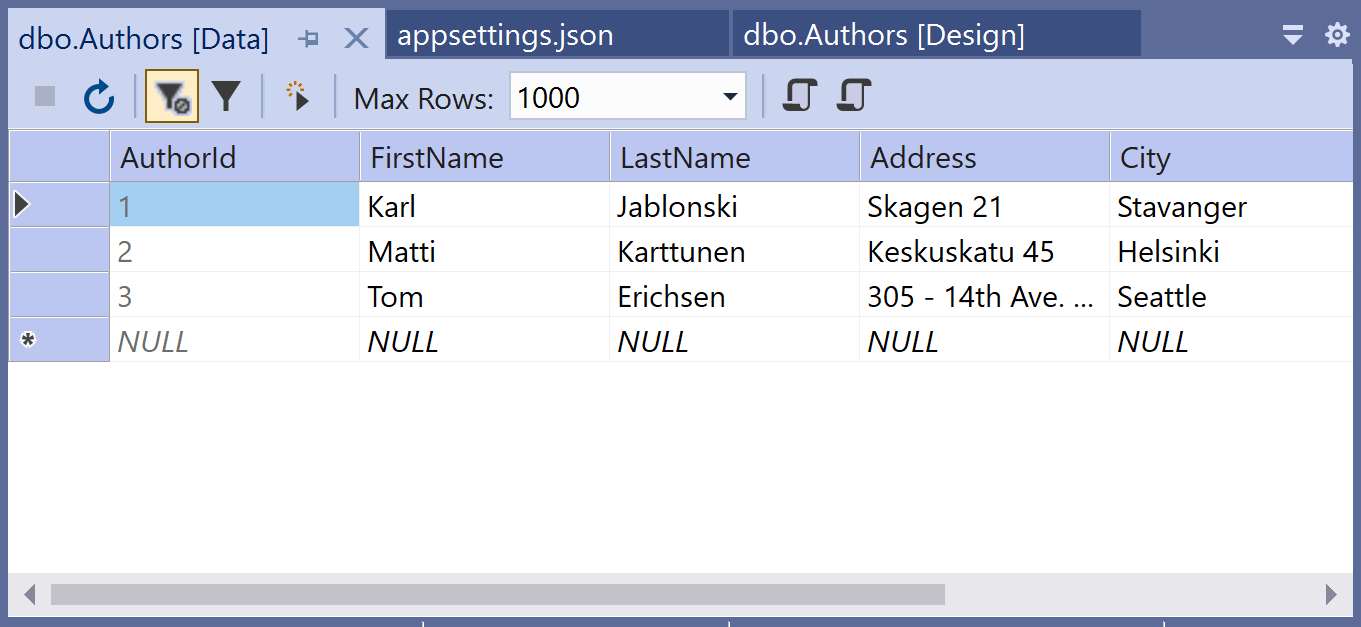
Setup Connection String
For local development, the ASP.NET Core configuration system reads the connection string from the appsettings.json file. So let's add the connection to that file as shown below.
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Data Source=(localdb)\\ProjectsV13;Initial Catalog=AuthorDb;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true"
},
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*"
}
The above connection string specifies that the application will use a LocalDB database named AuthorDb.mdf.
