C#
- Getting started with C# Language
- Learn Tutorial
- Overview
- Environment Setup
- Variables
- Data Types
- Strings
- Numbers
- User Input
- Arrays
- Multidimensional Arrays
- Methods
- Nullable Types
- Return Statement
- Conditional Statements
- Switch Statement
- While Loops
- For Loop
- Foreach Loop
- Break and Continue Statements
- Structure
- Enums
- Classes and Objects
- Comments
- Constructors
- Getters and Setters
- Static Members
- Static Class
- Operators
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Abstract Class
- Interfaces
- Exception Handling
- Regular Expressions
- File Handling
- Database Operations
- Delegates
- Events
- Collections
- Generics
- .NET Compiler Platform (Roslyn)
- Access Modifiers
- Access network shared folder with username and password
- Accessing Databases
- Action Filters
- Aliases of built-in types
- An overview of c# collections
- Anonymous types
- Arrays
- ASP.NET Identity
- AssemblyInfo.cs Examples
- Async/await, Backgroundworker, Task and Thread Examples
- Async-Await
- Asynchronous Socket
- Attributes
- BackgroundWorker
- BigInteger
- Binary Serialization
-
BindingList
- Built-in Types
- C# 3.0 Features
- C# 4.0 Features
- C# 5.0 Features
- C# 6.0 Features
- C# 7.0 Features
- C# Authentication handler
- C# Script
- Caching
- Casting
- Checked and Unchecked
- CLSCompliantAttribute
- Code Contracts
- Code Contracts and Assertions
- Collection Initializers
- Comments and regions
- Common String Operations
- Conditional Statements
- Constructors and Finalizers
- Creating a Console Application using a Plain-Text Editor and the C# Compiler (csc.exe)
- Creating Own MessageBox in Windows Form Application
- Creational Design Patterns
- Cryptography (System.Security.Cryptography)
- Data Annotation
- DateTime Methods
- Delegates
- Dependency Injection
- Diagnostics
- Dynamic type
- Enum
- Equality Operator
- Equals and GetHashCode
- Events
- Exception Handling
- Expression Trees
- Extension Methods
- File and Stream I/O
- FileSystemWatcher
- Func delegates
- Function with multiple return values
- Functional Programming
- Garbage Collector in .Net
- Generating Random Numbers in C#
- Generic Lambda Query Builder
- Generics
- Getting Started: Json with C#
- Guid
- Handling FormatException when converting string to other types
- Hash Functions
- How to Start Learning C# While Still in College
- How to use C# Structs to create a Union type (Similar to C Unions)
- ICloneable
- IComparable
- IDisposable interface
- IEnumerable
- ILGenerator
- Immutability
- Implementing Decorator Design Pattern
- Implementing Flyweight Design Pattern
- Import Google Contacts
- Including Font Resources
- Indexer
- Inheritance
- Initializing Properties
- INotifyPropertyChanged interface
- Interfaces
- Interoperability
- IQueryable interface
- Iterators
- Keywords
- Lambda expressions
- Lambda Expressions
- LINQ Queries
- Linq to Objects
- LINQ to XML
- Literals
- Lock Statement
- Looping
- Making a variable thread safe
- Methods
- Microsoft.Exchange.WebServices
- Named and Optional Arguments
- Named Arguments
- nameof Operator
- Naming Conventions
- Networking
- Nullable types
- Null-Coalescing Operator
- Null-conditional Operators
- NullReferenceException
- O(n) Algorithm for circular rotation of an array
- Object initializers
- Object Oriented Programming In C#
-
ObservableCollection
- Operators
- Overflow
- Overload Resolution
- Parallel LINQ (PLINQ)
- Partial class and methods
- Performing HTTP requests
- Pointers
- Pointers & Unsafe Code
- Polymorphism
- Preprocessor directives
- Properties
- Reactive Extensions (Rx)
- Read & Understand Stacktraces
- Reading and writing .zip files
- Recursion
- Reflection
- Regex Parsing
- Runtime Compile
- Singleton Implementation
- Static Classes
- Stopwatches
- Stream
- String Concatenate
- String Escape Sequences
- String Interpolation
- String Manipulation
- String.Format
- StringBuilder
- Structs
- Structural Design Patterns
- Synchronization Context in Async-Await
- System.DirectoryServices.Protocols.LdapConnection
- System.Management.Automation
- T4 Code Generation
- Task Parallel Library
- Task Parallel Library (TPL) Dataflow Constructs
- Threading
- Timers
- Tuples
- Type Conversion
- Unsafe Code in .NET
- Using Directive
- Using json.net
- Using SQLite in C#
- Using Statement
- Value type vs Reference type
- Verbatim Strings
- Windows Communication Foundation
- XDocument and the System.Xml.Linq namespace
- XML Documentation Comments
- XmlDocument and the System.Xml namespace
- Yield Keyword
C# Data Types
C# is a strongly-typed language and we must declare the type of a variable that indicates the kind of values it is going to store, such as integer, float, decimal, text, etc.
The types of C# language are divided into two main categories.
- Value types
- Reference types.
Value Types
A value type holds a data value within its own memory space and it directly contains the values. Let's take the following example
int num = 99;
The system will stores 99 in the memory space allocated for the variable num.
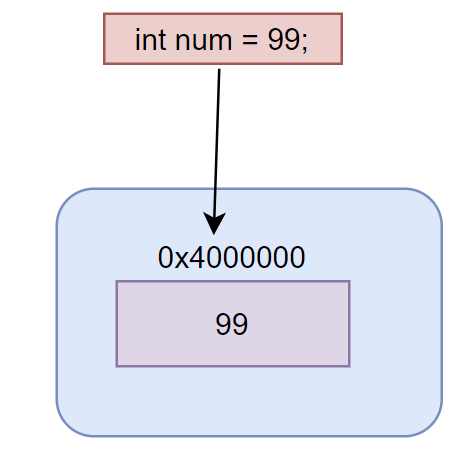
The value types include simple types such as, int, float, bool, and char, enum, struct, and Nullable value types. These data types are called primitive (built-in types), because they are embedded in C# language at the lowest level.
| Data Type | Description | Range |
|---|---|---|
| byte | 8-bit unsigned integer | 0 to 255 |
| sbyte | 8-bit signed integer | -128 to 127 |
| short | 16-bit signed integer | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| ushort | 16-bit unsigned integer | 0 to 65,535 |
| int | 32-bit signed integer | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| uint | 32-bit unsigned integer | 0 to 4,294,967,295 |
| long | 64-bit signed integer | -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 |
| ulong | 64-bit unsigned integer | 0 to 18,446,744,073,709,551,615 |
| float | 32-bit Single-precision floating point type | -3.402823e38 to 3.402823e38 |
| double | 64-bit double-precision floating point type | -1.79769313486232e308 to 1.79769313486232e308 |
| decimal | 128-bit decimal type for financial and monetary calculations | (+ or -)1.0 x 10e-28 to 7.9 x 10e28 |
| char | 16-bit single Unicode character | Any valid character, e.g. a,*, \x0058 (hex), or\u0058 (Unicode) |
| bool | 8-bit logical true/false value | True or False |
| object | Base type of all other types. | |
| string | A sequence of Unicode characters | |
| DateTime | Represents date and time | 0:00:00am 1/1/01 to 11:59:59pm 12/31/9999 |
Reference Types
The reference type contains a pointer to another memory location that holds the data. It doesn't store its value directly unlike value types, but it stores the address where the value is being stored. The reference types include class, interface, delegate, and array types.
string message = "Welcome to C# Tutorial.";
The system will select a random location in memory for the variable message. The value of a variable message is the memory address of the actual data value.
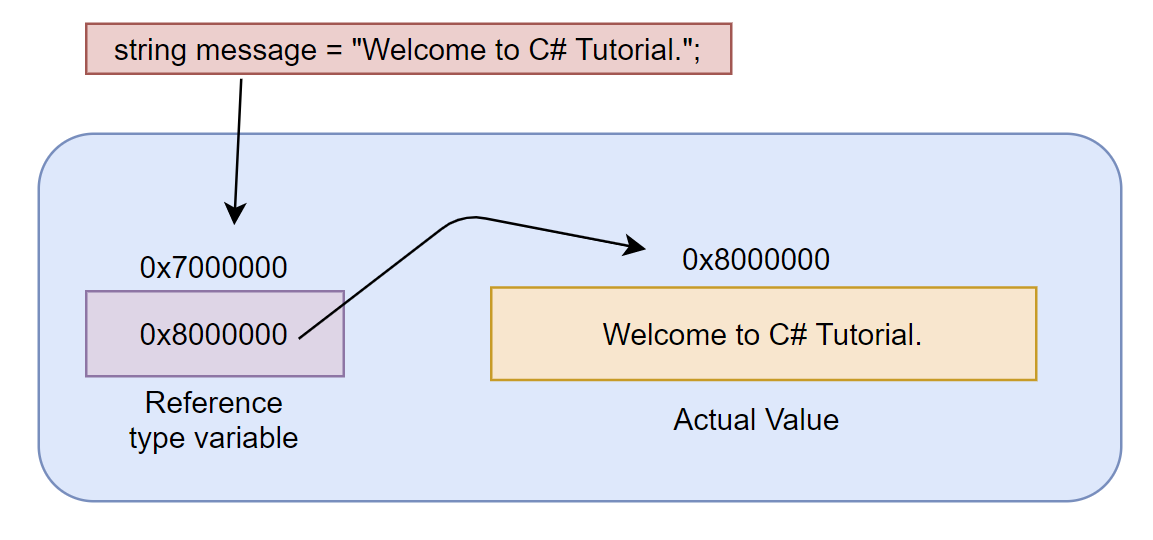
Thus, reference type stores the address of the location where the actual value is stored instead of the value itself.
