C# Database Operations
Nowadays, you can't imagine any application without a database. If your application needs to access data from the database, you will need to perform some database operations.
- In any programming language, accessing Data from a database is one of the important aspects.
- It is an absolute necessity for any programming language to have the ability to work with databases.
- C# can work with a majority of databases, the most common database is Microsoft SQL Server.
SqlConnection
C# provides a SqlConnection class which represents a connection to a SQL Server database, it cannot be inherited.
- A
SqlConnectionobject represents a unique session to a SQL Server data source. - With a client/server database system, it is equivalent to a network connection to the server.
- It is used together with
SqlDataAdapterandSqlCommandto increase performance when connecting to a Microsoft SQL Server database.
Create Database
To create a database, let's open the SQL Server Object Explorer, expand the SQL Server and right-click on the Databases and select the Add New Database.
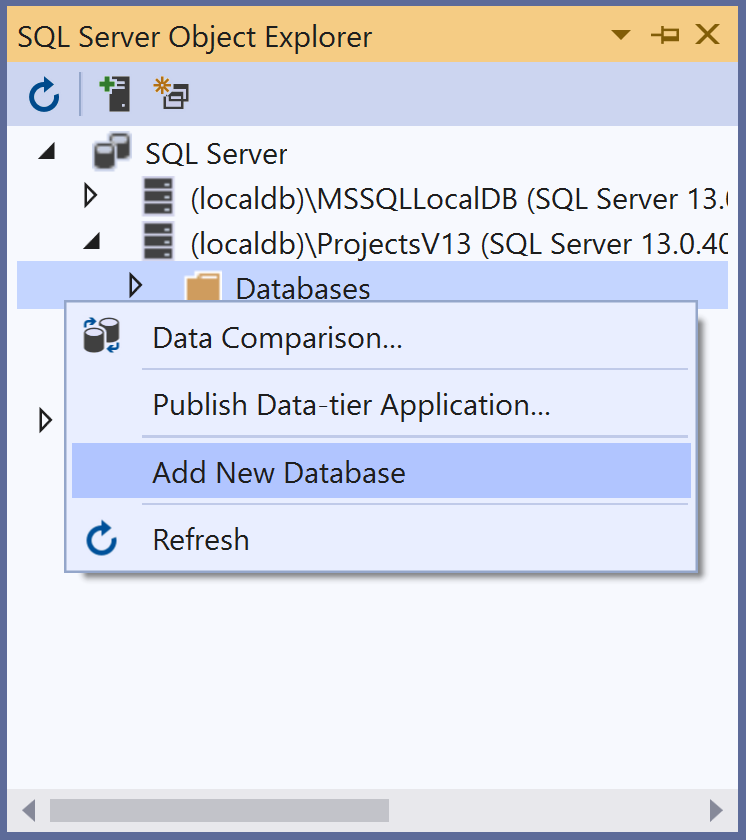
It will open the Create Database dialog.
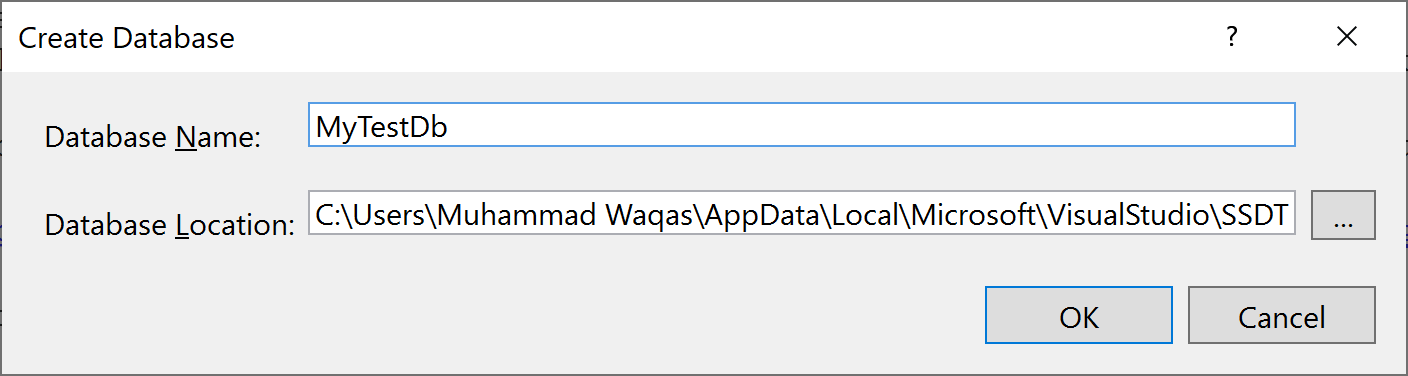
Enter the database name such as MyTestDb and click the Ok button. Now right-click on the newly created database and select New Query... It will open the query editor, let's run the following script in the query editor.
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Authors] (
[AuthorId] INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
[Name] NVARCHAR (MAX) NULL
);
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Authors] VALUES (1, 'Mark');
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Authors] VALUES (2, 'John');
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Authors] VALUES (3, 'Stella');
It will create a table with the name Authors and add three records to that table. To check the data in the database table, right-click on the Authors table in SQL Server Object Explorer.
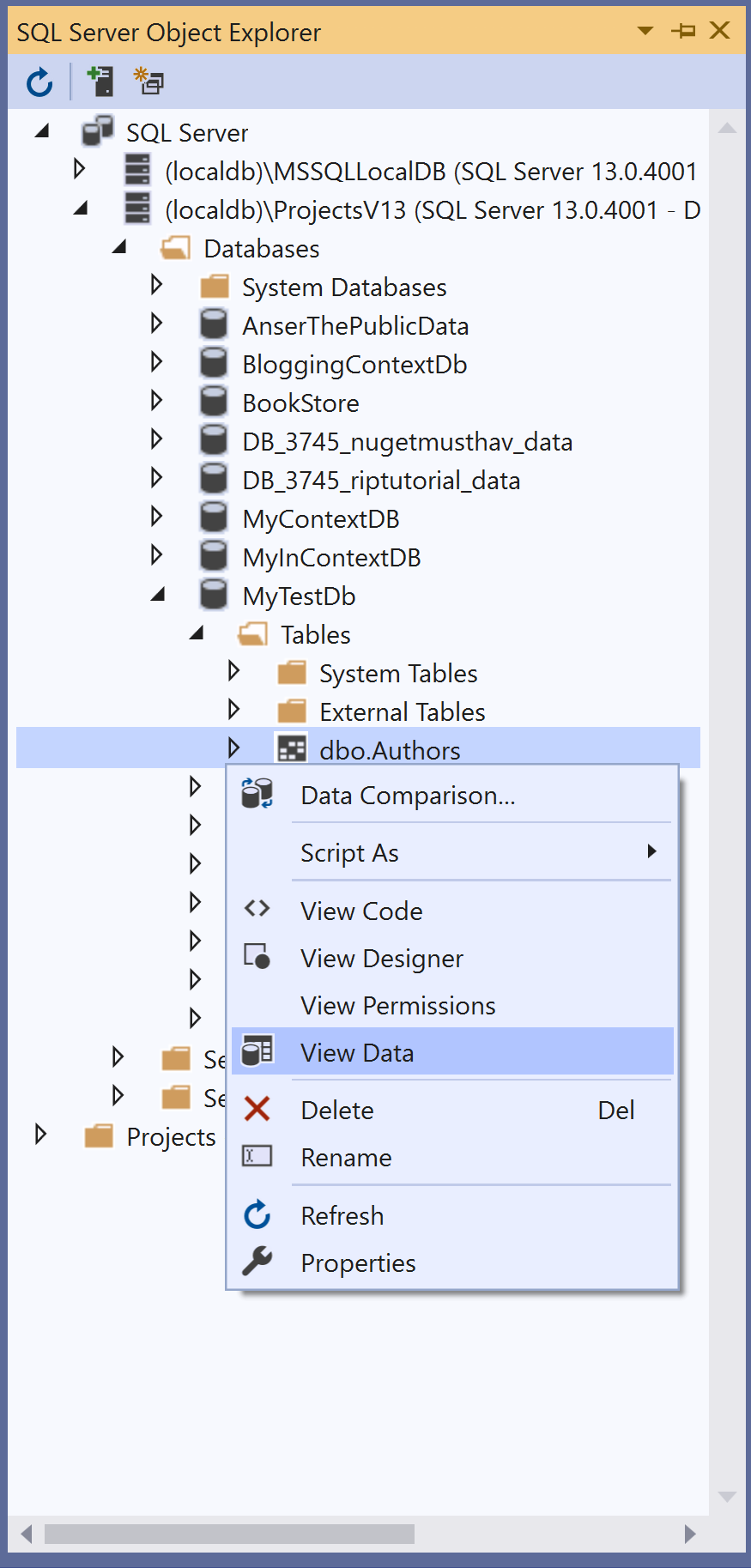
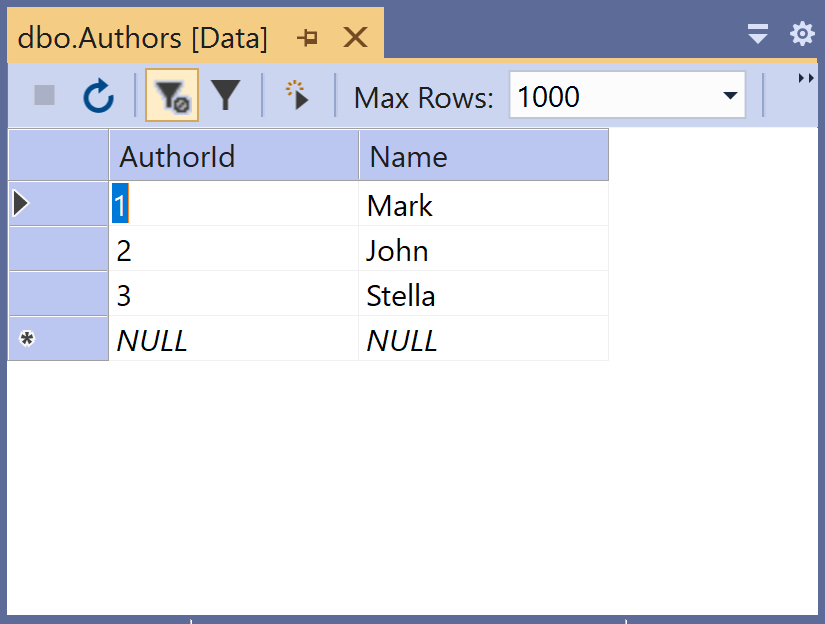
Select the View Data option and it will display all the records.
Connect Database
To connect to the SQL database, you can use the following code.
string connectionString = @"Data Source=(localdb)\ProjectsV13;Initial Catalog=MyTestDb;Integrated Security=True;";
using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
connection.Open();
// code here
}
The above code will create a new connection to the SQL Server database that will be connected using the connection string. To ensure that connections are always closed, open the connection inside of a using block.
Read Data From Database
Let's add some code to read data from the database we created.
string connectionString = @"Data Source=(localdb)\ProjectsV13;Initial Catalog=MyTestDb;Integrated Security=True;";
using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
connection.Open();
string sql = "SELECT * FROM Authors";
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(sql, connection);
SqlDataReader dreader = cmd.ExecuteReader();
// for one by one reading row
while (dreader.Read())
{
Console.WriteLine(dreader.GetValue(0) + ", " + dreader.GetValue(1));
}
}
Let's run the above code and you will see the following output.
1, Mark
2, John
3, Stella
Write Data to Database
Now let's insert one more record into the database and then read all the records using the following code.
string connectionString = @"Data Source=(localdb)\ProjectsV13;Initial Catalog=MyTestDb;Integrated Security=True;";
using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
connection.Open();
// Insert one more record to the database
string sql = "INSERT INTO [dbo].[Authors] VALUES (4, 'Smith')";
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(sql, connection);
SqlDataAdapter adap = new SqlDataAdapter();
adap.InsertCommand = new SqlCommand(sql, connection);
adap.InsertCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
//Read all records from the database
sql = "SELECT * FROM Authors";
cmd = new SqlCommand(sql, connection);
SqlDataReader dreader = cmd.ExecuteReader();
// for one by one reading row
while (dreader.Read())
{
Console.WriteLine(dreader.GetValue(0) + ", " + dreader.GetValue(1));
}
}
Let's run the above code and you will see the following output.
1, Mark
2, John
3, Stella
4, Smith
For more information about file handling, visit https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/system.data.sqlclient.sqlconnection
All the examples related to the database operations are available in the DatabaseOperations.cs file of the source code. Download the source code and try out all the examples for better understanding.
